Comparative genomics and transcriptomics analysis of the bHLH gene family indicate their roles in regulating flavonoid biosynthesis in Sophora flavescens
- PMID: 39381512
- PMCID: PMC11458398
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1445488
Comparative genomics and transcriptomics analysis of the bHLH gene family indicate their roles in regulating flavonoid biosynthesis in Sophora flavescens
Abstract
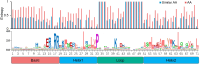
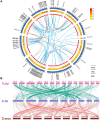
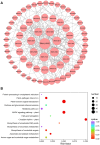
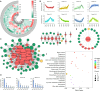
The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors play crucial roles in various processes, such as plant development, secondary metabolism, and response to biotic/abiotic stresses. Sophora flavescens is a widely used traditional herbal medicine in clinical practice, known for its abundant flavonoids as the main active compounds. However, there has been no comprehensive analysis of S. flavescens bHLH (SfbHLH) gene family reported currently. In this study, we identified 167 SfbHLH genes and classified them into 23 subfamilies based on comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis. Furthermore, widespread duplications significantly contributed to the expansion of SfbHLH family. Notably, SfbHLH042 was found to occupy a central position in the bHLH protein-protein interaction network. Transcriptome analysis of four tissues (leaf, stem, root and flower) revealed that most SfbHLH genes exhibited high expression levels exclusively in specific tissues of S. flavescens. The integrated analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics during pod development stages revealed that SfbHLH042 may play a central role in connecting SfbHLH genes, flavonoids, and key enzymes involved in the biosynthesis pathway. Moreover, we also checked the expression of 8 SfbHLH genes using RT-qPCR analysis to realize the expression profiles of these genes among various tissues at different cultivated periods and root development. Our study would aid to understand the phylogeny and expression profile of SfbHLH family genes, and provide a promising candidate gene, SfbHLH042, for regulating the biosynthesis of flavonoids in S. flavescens.
Keywords: Sophora flavescens; bHLH; coexpression network; flavonoid biosynthesis; gene duplication.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Lu, Song, Wang, Wang, Lei, Liu, Lei and Niu.
Conflict of interest statement
Author ZL was employed by Shanxi Zhendong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Baudry A., Caboche M., Lepiniec L. (2006). TT8 controls its own expression in a feedback regulation involving TTG1 and homologous MYB and bHLH factors, allowing a strong and cell-specific accumulation of flavonoids in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant J. 46, 768–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02733.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

