Pathogenic Huntingtin aggregates alter actin organization and cellular stiffness resulting in stalled clathrin-mediated endocytosis
- PMID: 39382268
- PMCID: PMC11643626
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.98363
Pathogenic Huntingtin aggregates alter actin organization and cellular stiffness resulting in stalled clathrin-mediated endocytosis
Abstract
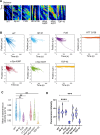
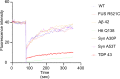
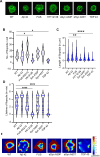
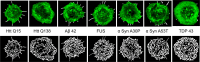
Aggregation of mutant forms of Huntingtin is the underlying feature of neurodegeneration observed in Huntington's disorder. In addition to neurons, cellular processes in non-neuronal cell types are also shown to be affected. Cells expressing neurodegeneration-associated mutant proteins show altered uptake of ligands, suggestive of impaired endocytosis, in a manner as yet unknown. Using live cell imaging, we show that clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) is affected in Drosophila hemocytes and mammalian cells containing Huntingtin aggregates. This is also accompanied by alterations in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton resulting in increased cellular stiffness. Further, we find that Huntingtin aggregates sequester actin and actin-modifying proteins. Overexpression of Hip1 or Arp3 (actin-interacting proteins) could restore CME and cellular stiffness in cells containing Huntingtin aggregates. Neurodegeneration driven by pathogenic Huntingtin was also rescued upon overexpression of either Hip1 or Arp3 in Drosophila. Examination of other pathogenic aggregates revealed that TDP-43 also displayed defective CME, altered actin organization and increased stiffness, similar to pathogenic Huntingtin. Together, our results point to an intimate connection between dysfunctional CME, actin misorganization and increased cellular stiffness caused by alteration in the local intracellular environment by pathogenic aggregates.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; actin; aggregates; cell biology; clathrin; neurodegeneration; stiffness; trafficking.
© 2024, Singh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SS, SR, AS, SK, PD, VA, AN, SP, AM, DS No competing interests declared
Figures

Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.07.10.548473
References
-
- Biancospino M, Buel GR, Niño CA, Maspero E, Scotto di Perrotolo R, Raimondi A, Redlingshöfer L, Weber J, Brodsky FM, Walters KJ, Polo S. Clathrin light chain A drives selective myosin VI recruitment to clathrin-coated pits under membrane tension. Nature Communications. 2019;10:4974. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12855-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

