Development of an orthotopic medulloblastoma zebrafish model for rapid drug testing
- PMID: 39383211
- PMCID: PMC11889719
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noae210
Development of an orthotopic medulloblastoma zebrafish model for rapid drug testing
Abstract
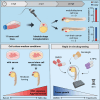
Background: Medulloblastoma (MB) is one of the most common malignant brain tumors in children. Current preclinical in vivo model systems for MB have increased our understanding of molecular mechanisms regulating MB development. However, they may not be suitable for large-scale studies. The aim of this study was to investigate if a zebrafish-based xenograft model can recapitulate MB growth and enable rapid drug testing.
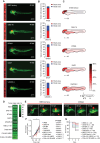
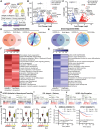
Methods: Nine different MB cell lines or patient-derived cells were transplanted into blastula-stage zebrafish embryos. Tumor development and migration were then monitored using live imaging. RNA sequencing was performed to investigate transcriptome changes after conditioning cells in a neural stem cell-like medium. Furthermore, drug treatments were tested in a 96-well format.
Results: We demonstrate here that transplantation of MB cells into the blastula stage of zebrafish embryos leads to orthotopic tumor growth that can be observed within 24 h after transplantation. Importantly, the homing of transplanted cells to the hindbrain region and the aggressiveness of tumor growth are enhanced by pre-culturing cells in a neural stem cell-like medium. The change in culture conditions rewires the transcriptome toward a more migratory and neuronal phenotype, including the expression of guidance molecules SEMA3A and EFNB1, both of which correlate with lower overall survival in MB patients. Furthermore, we highlight that the orthotopic zebrafish MB model has the potential to be used for rapid drug testing.
Conclusions: Blastula-stage zebrafish MB xenografts present an alternative to current MB mouse xenograft models, enabling quick evaluation of tumor cell growth, neurotropism, and drug efficacy.
Keywords: medulloblastoma; neurotropism; patient-derived xenografts; rapid drug testing; zebrafish.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors N.v.B., A.S.O., L.Z., L.Bo., B.C., F.J.S., J.I.J., and M.W. declare no conflict of interest. The authors S.L. and L.Br. received funding from the Karolinska Institutet core facility grant as well as user fees that are paid to the zebrafish core facility.
Figures




References
-
- Packer RJ, Gajjar A, Vezina G, et al. Phase III study of craniospinal radiation therapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy for newly diagnosed average-risk medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(25):4202–4208. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

