Focus on leveling the hidden: managing impacted maxillary canines
- PMID: 39383375
- PMCID: PMC11457965
- DOI: 10.1590/2177-6709.29.5.e24spe5
Focus on leveling the hidden: managing impacted maxillary canines
Abstract
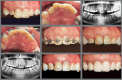
Introduction: The long pathway that the canines take as they emerge into the maxillary arch makes them vulnerable to disruption during their natural emergence time. The process of planning treatment for impacted maxillary canine (IMC) presents significant challenges, underscoring the need for careful consideration and expertise.
Objective: The aim of this article was to shed light on these complexities by discussing clinical case studies involving IMC, providing insights into the intricacies of their management.
Conclusions: The management of IMC within orthodontics presents a multifaceted challenge that include the necessity for precise diagnostic processes, prudent use of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), the strategic selection between open and closed exposure techniques, a in-depth understanding of the specific orthodontic biomechanics involved, and a keen awareness of potential adverse outcomes such as ankylosis, prolonged treatment times, root resorption, and additional complications.
Introdução:: O longo caminho que os caninos percorrem até irromper na arcada superior os torna vulneráveis a interrupções durante a erupção fisiológica. A etapa de planejamento do tratamento para caninos superiores impactados (CSI) apresenta desafios significativos, destacando a necessidade de consideração cuidadosa e expertise.
Objetivo:: O objetivo do presente artigo é esclarecer esses aspectos, discutindo relatos de casos clínicos envolvendo CSI, fornecendo percepções sobre a complexidade de seu manejo.
Conclusões:: O manejo do CSI na Ortodontia apresenta um desafio multifacetado, que inclui a necessidade de um diagnóstico preciso, o uso prudente de tomografia computadorizada de feixe cônico (TCFC), a seleção estratégica entre as técnicas de exposição aberta ou fechada, uma compreensão aprofundada da biomecânica ortodôntica específica envolvida, e uma consciência ampla dos possíveis resultados adversos, como anquilose, tempo de tratamento prolongado, reabsorção radicular e complicações adicionais.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no commercial, proprietary or financial interest in the products or companies described in this article.
Figures

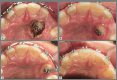
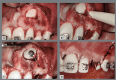
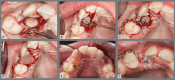

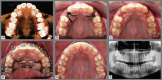










References
-
- Kim Y, Hyun HK, Jang KT. Interrelationship between the position of impacted maxillary canines and the morphology of the maxilla. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012;141(5):556–562. - PubMed
-
- Koç A, Kaya S, Abdulsalam WA. Three-dimensional analysis of impacted maxillary and mandibular canines and evaluation of factors associated with transmigration on cone-beam computed tomography images. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;79(3):538.e1–538.11. - PubMed
-
- Ucar FI, Celebi AA, Tan E, Topcuoglu T, Sekerci AE. Effects of impacted maxillary canines on root resorption of lateral incisors a cone beam computed tomography study. J Orofac Orthop. 2017;78(3):233–240. - PubMed
-
- Bedoya MM, Park JH. A review of the diagnosis and management of impacted maxillary canines. J Am Dent Assoc. 2009;140(12):1485–1493. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

