Global research and current trends on nanotherapy in lung cancer research: a bibliometric analysis of 20 years
- PMID: 39384612
- PMCID: PMC11465009
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01332-2
Global research and current trends on nanotherapy in lung cancer research: a bibliometric analysis of 20 years
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer ranks as one of the most rapidly growing malignancies. Which is characterized by its poor prognosis and a low survival rate due to late diagnosis and limited efficacy of conventional treatments. In recent years nanotechnology has emerged as a promising frontier in the management of lung cancer, presenting novel strategies to enhance drug administration, improve therapeutic efficiency, and mitigate side effects. This research comprehensively evaluates the current state and research trends concerning the application of nanomaterials in lung cancer through bibliometric analysis.
Materials and methods: We employed a systematic approach by retrieving studies from the Scopus database that focused on nanomaterials and lung cancer between 2003 and 2023. Subsequently, we carefully selected relevant articles based on predetermined inclusion criteria. The selected publications were then subjected to bibliometric and visual analysis using softwares such as VOSviewer and Biblioshiny.
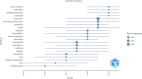
Results: A total of 3523 studies that meet inclusion criteria were selected for bibliometric analysis. We observed a progressive increase in the number of annual publications from 2003 to 2023, indicating the growing interest in this field. According to our analysis, China is the primary contributor to publication output among the countries. The "Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China" was the most influential institution. Among the authors, "Dr. Jack A. Roth" and "Dr. Huang Leaf" had the highest number of publications and cited publications, respectively. The "International Journal of Nanomedicine" was found to be the most prolific journal in this field. Additionally, "Biomaterials" emerged as the most cited journal. Through keyword analysis, we identified five main research themes and future research directions; nono-immunotherapy and green synthesis are the hot topics in this research field.
Conclusion: Our study summarized the key characteristics of publications in this field and identified the most influential countries, institutions, authors, journals, hot topics, and trends related to the application of nanomaterials in lung cancer. These findings contribute to the existing body of knowledge and serve as a foundation for future research endeavors in this area. More effective efforts are needed in this field to reduce the burden of lung cancer and help achieve the United Nation's Sustainable Development Goals.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; Lung cancer research; Nanomaterials; Scopus database.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
