Rare variant contribution to the heritability of coronary artery disease
- PMID: 39384761
- PMCID: PMC11464707
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52939-6
Rare variant contribution to the heritability of coronary artery disease
Abstract
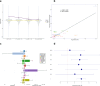
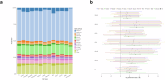
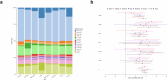
Whole genome sequences (WGS) enable discovery of rare variants which may contribute to missing heritability of coronary artery disease (CAD). To measure their contribution, we apply the GREML-LDMS-I approach to WGS of 4949 cases and 17,494 controls of European ancestry from the NHLBI TOPMed program. We estimate CAD heritability at 34.3% assuming a prevalence of 8.2%. Ultra-rare (minor allele frequency ≤ 0.1%) variants with low linkage disequilibrium (LD) score contribute ~50% of the heritability. We also investigate CAD heritability enrichment using a diverse set of functional annotations: i) constraint; ii) predicted protein-altering impact; iii) cis-regulatory elements from a cell-specific chromatin atlas of the human coronary; and iv) annotation principal components representing a wide range of functional processes. We observe marked enrichment of CAD heritability for most functional annotations. These results reveal the predominant role of ultra-rare variants in low LD on the heritability of CAD. Moreover, they highlight several functional processes including cell type-specific regulatory mechanisms as key drivers of CAD genetic risk.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P.T.E. receives sponsored research support from Bayer AG, IBM Research, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer and Novo Nordisk; he has also served on advisory boards or consulted for Bayer AG, MyoKardia and Novartis. B.M.P. serves on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. L.M.R. is a consultant for the TOPMed Administrative Coordinating Center (through Westat). C.L.M. received grant support from AstraZeneca for unrelated work. R.D. reported being a scientific co-founder, consultant and equity holder for Pensieve Health and being a consultant for Variant Bio, all not related to this work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Tsao, C. W. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2023 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation147, e93–e621 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Wienke, A., Holm, N. V., Skytthe, A. & Yashin, A. I. The heritability of mortality due to heart diseases: a correlated frailty model applied to danish twins. Twin Res.4, 266–274 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Zdravkovic, S. et al. Heritability of death from coronary heart disease: a 36-year follow-up of 20 966 Swedish twins. J. Intern. Med.252, 247–254 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Chen, Z. & Schunkert, H. Genetics of coronary artery disease in the post‐GWAS era. J. Intern. Med.290, 980–992 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM124836/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139865/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028747/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146860/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500014C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL167072/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055673/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100037C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112064/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003273/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008853/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500015C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL164577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201600033C/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL139865, R01-HL155915/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- UL1 TR004419/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148239/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL157635/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005831/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35-GM124836/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01 HL155915/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

