Modeling transmission mechanism to infer treatment efficacy of different drugs and combination therapy against Trichuris trichiura
- PMID: 39384803
- PMCID: PMC11464734
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-73164-7
Modeling transmission mechanism to infer treatment efficacy of different drugs and combination therapy against Trichuris trichiura
Abstract
Trichuris trichiura is one of four soil-transmitted helminth species that, collectively, are responsible for a considerable public health burden. The World Health Organization recommends preventive chemotherapy as the main intervention to eliminate soil-transmitted helminthiasis as a public health problem. Clinical trials estimated the efficacy of different drugs and treatment regimen against T. trichiura and other soil-transmitted helminth species, whilst meta-analyses and modeling efforts were conducted to determine the most efficacious drugs and drug combinations. Of note, the diagnostic error was often neglected, and hence, cure rates (CRs) might be overestimated. We developed a Bayesian model, which estimates drug efficacy against T. trichiura, taking into account the transmission mechanism and the diagnostic error. The model was fitted to individual-level egg count data from an ensemble of seven trials with 29 treatments. We estimated the 'true' CRs, which were consistently lower than those reported in the literature. In our analysis, the treatment with the highest CR was combination therapy of albendazole plus pyrantel pamoate plus oxantel pamoate with a CR of 79% and an egg reduction rate (ERR) of 91%. Albendazole plus oxantel pamoate showed the highest ERR of 97% and a CR of 69%. Additionally, we estimated the intensity-dependent sensitivity of the Kato-Katz technique. For 24 eggs per gram of stool, the sensitivity was around 50% for a single Kato-Katz thick smear and increased to almost 70% for duplicate Kato-Katz thick smears. Combination therapies against soil-transmitted helminthiasis should be considered and the evaluation of infection intensity in low transmission settings via multiple Kato-Katz thick smears is recommended.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
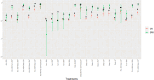
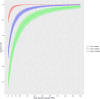
References
-
- World Health Organization. Soil-transmitted helminth infections. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helmin... (2019). Accessed 10 Mar 2023.
-
- World Health Organization. 2030 targets for soil-transmitted helminthiases control programmes. http://www.who.int/intestinal_worms/resources/9789240000315/en/. Accessed 10 Mar 2023.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

