Biomolecular condensates mediate bending and scission of endosome membranes
- PMID: 39385023
- PMCID: PMC11525194
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07990-0
Biomolecular condensates mediate bending and scission of endosome membranes
Abstract
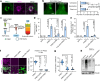
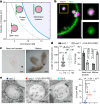
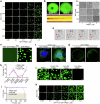
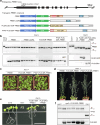
Multivesicular bodies are key endosomal compartments implicated in cellular quality control through their degradation of membrane-bound cargo proteins1-3. The ATP-consuming ESCRT protein machinery mediates the capture and engulfment of membrane-bound cargo proteins through invagination and scission of multivesicular-body membranes to form intraluminal vesicles4,5. Here we report that the plant ESCRT component FREE16 forms liquid-like condensates that associate with membranes to drive intraluminal vesicle formation. We use a minimal physical model, reconstitution experiments and in silico simulations to identify the dynamics of this process and describe intermediate morphologies of nascent intraluminal vesicles. Furthermore, we find that condensate-wetting-induced line tension forces and membrane asymmetries are sufficient to mediate scission of the membrane neck without the ESCRT protein machinery or ATP consumption. Genetic manipulation of the ESCRT pathway in several eukaryotes provides additional evidence for condensate-mediated membrane scission in vivo. We find that the interplay between condensate and machinery-mediated scission mechanisms is indispensable for osmotic stress tolerance in plants. We propose that condensate-mediated scission represents a previously undescribed scission mechanism that depends on the physicomolecular properties of the condensate and is involved in a range of trafficking processes. More generally, FREE1 condensate-mediated membrane scission in multivesicular-body biogenesis highlights the fundamental role of wetting in intracellular dynamics and organization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




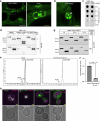
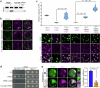
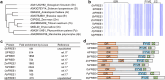


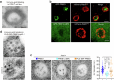

Comment in
-
Biomolecular condensates modulate membrane remodeling.Mol Plant. 2025 Jan 6;18(1):17-18. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2024.11.009. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Mol Plant. 2025. PMID: 39573881 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

