Exosomal miR-106a-5p from highly metastatic colorectal cancer cells drives liver metastasis by inducing macrophage M2 polarization in the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 39385295
- PMCID: PMC11462797
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-024-03204-7
Exosomal miR-106a-5p from highly metastatic colorectal cancer cells drives liver metastasis by inducing macrophage M2 polarization in the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
Background: The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a dynamic system orchestrated by intricate cell-to-cell crosstalk. Specifically, macrophages within the TME play a crucial role in driving tumor progression. Exosomes are key mediators of communication between tumor cells and the TME. However, the mechanisms underlying exosome-driven crosstalk between tumor cells and macrophages during colorectal cancer (CRC) progression remain incompletely elucidated.
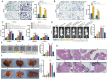
Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing were analyzed using the Seurat package. Exosomes were isolated using ultracentrifugation and characterized by transmission electron microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis, and western blot. miRNAs differentially expressed in exosomes were analyzed using the limma package. CD206 expression in CRC tissues, exosomes tracing, and exosomal miR-106a-5p transport were observed through immunofluorescence. Macrophage polarization was assessed via qRT-PCR, ELISA, and flow cytometry. The interactions between miR-106a-5p, hnRNPA1, and SOCS6 were evaluated using miRNA pull-down, RIP, and dual-luciferase reporter assays. Transwell assays and liver metastasis model explored the role of exosomal miR-106a-5p-induced M2 macrophages in promoting CRC liver metastasis.
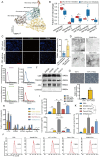
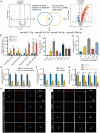
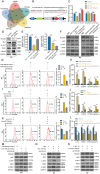
Result: The proportion of M2 macrophages is increased in CRC with liver metastasis compared to those without. Highly metastatic CRC cells release exosomes enriched with miR-106a-5p, which promote macrophages M2 polarization by suppressing SOCS6 and activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway. These M2 macrophages reciprocally enhance CRC liver metastasis. hnRNPA1 regulate the transport of miR-106a-5p into exosomes. Clinically, elevated miR-106a-5p in plasma exosomes correlated with liver metastasis and poor prognosis.
Conclusion: CRC-derived exosomal miR-106a-5p plays a critical role in promoting liver metastasis and is a potential biomarker for the prevention and treatment of CRC liver metastasis.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Exosomes; Liver metastasis; Macrophage; miRNAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Margonis GA, Sergentanis TN, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Andreatos N, Tzanninis IG, Sasaki K, et al. Impact of Surgical Margin Width on recurrence and overall survival following R0 hepatic resection of colorectal metastases: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2018;267:1047–55. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

