Wide Restorative Emergence Angle Increases Marginal Bone Loss and Impairs Integrity of the Junctional Epithelium of the Implant Supracrestal Complex: A Preclinical Study
- PMID: 39385502
- PMCID: PMC11651719
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.14070
Wide Restorative Emergence Angle Increases Marginal Bone Loss and Impairs Integrity of the Junctional Epithelium of the Implant Supracrestal Complex: A Preclinical Study
Abstract
Aim: To assess the influence of the emergence angle on marginal bone loss (MBL) and supracrestal soft tissue around dental implants.
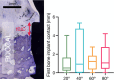
Materials and methods: In six mongrel dogs, the mandibular premolars and molars were extracted. After 3 months of healing, four dental implants were placed in each hemimandible. The implants were randomly allocated to receive one of four customized healing abutments, each with a different value of the restorative emergence angle: 20°, 40°, 60° or 80°. Intra-oral radiographs were taken after placing the healing abutments and at 6, 9, 16 and 24 weeks of follow-up. Then, micro-CT and undecalcified histology and synchrotron were performed. MBL over time was analysed with generalized estimating equations (GEEs) and adjusted for baseline soft-tissue thickness.
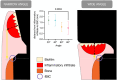
Results: From implant placement to 24 weeks, GEE modelling showed that the MBL at mesial and distal sites consistently increased over time, indicating MBL in all groups (p < 0.001). The model indicated that MBL varied significantly across the different restorative angles (angle effect, p < 0.001), with 80° showing the greatest bone loss. Micro-CT, histology and synchrotron confirmed the corresponding trends and showed that wide restorative angles (60° and 80°) impaired the integrity of the junctional epithelium of the supracrestal tissue.
Conclusions: A wide restorative angle increases MBL and impairs the integrity of the junctional epithelium of the implant supracrestal complex.
Keywords: CAD/CAM; dental implant; dental implant‐abutment design; emergence profile; histology; prosthodontics; restorative angle; titanium abutments.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Clinical Periodontology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Albrektsson, T. , Zarb G., Worthington P., and Eriksson A. R.. 1986. “The Long‐Term Efficacy of Currently Used Dental Implants: A Review and Proposed Criteria of Success.” The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 1, no. 1: 11–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

