Persistence of hepatitis B surface antibody until 7 years of age following administration of hexavalent and pentavalent vaccines in children at 2, 4, 6, and 18 months
- PMID: 39385752
- PMCID: PMC11462280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2024.100561
Persistence of hepatitis B surface antibody until 7 years of age following administration of hexavalent and pentavalent vaccines in children at 2, 4, 6, and 18 months
Abstract
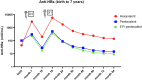
Thailand incorporated the hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine into the infant combination vaccine known as pentavalent wP-containing vaccines (DTwP-HB-Hib) and hexavalent aP-containing vaccines (DTaP-IPV-HB-Hib). We followed healthy children from the clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02408926) in which children were randomly assigned to receive either pentavalent or hexavalent vaccines for their primary series (administered at 2, 4, and 6 months) and first booster vaccination (at 18 months), following the monovalent HepB vaccine at birth. Blood samples were collected to evaluate the persistence of hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs) at 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 years of age. The results showed that at 7 years of age, a higher percentage of children in the hexavalent group maintained anti-HBs levels ≥ 10 mIU/mL compared to those in the pentavalent group (86.9 % vs. 59.7 %). This study showed good persistence of anti-HBs among hexavalent-vaccinated children 5.5 years after the last dose of the HepB vaccine.
Keywords: Antibody; Childhood; Hepatitis; Hexavalent; Pentavalent; Vaccine.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Wanlapakorn N., Pruetarat N., Sarawanangkoor N., Phanphanit K., Srimuan D., Thatsanathorn T., et al. Immunogenicity of the pentavalent DTwP-HB-Hib vaccine (Shan-5) used in the Thai Expanded Program on Immunization compared to the hexavalent DTaP-HB-Hib-IPV and DTwP-HB-Hib (Quinvaxem) vaccines administered to infants at 2, 4, 6 months of age. Vaccine. 2023;41:3855–3861. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.05.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Posuwan N., Wanlapakorn N., Vongpunsawad S., Sintusek P., Leuridan E., Van Damme P., et al. Comparison of hepatitis B surface antibody levels induced by the pentavalent DTwP-HB-Hib versus the hexavalent DTaP-HB-Hib-IPV vaccine, administered to infants at 2, 4, 6, and 18 months of age, following monovalent hepatitis B vaccination at birth. Vaccine. 2020;38:1643–1651. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.12.065. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wanlapakorn N., Sarawanangkoor N., Srimuan D., Thatsanathorn T., Thongmee T., Poovorawan Y. Antibody persistence to diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, Bordetella pertussis antigens, and Haemophilus influenzae type b following primary and first booster with pentavalent versus hexavalent vaccines. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024;20:2352909. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2352909. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

