A review of the electrochemical and galvanic corrosion behavior of important intermetallic compounds in the context of aluminum alloys
- PMID: 39385762
- PMCID: PMC11462131
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra06070a
A review of the electrochemical and galvanic corrosion behavior of important intermetallic compounds in the context of aluminum alloys
Abstract
Aluminum alloys are widely sought for different applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio. Most often this increased strength of the alloy is achieved by specific alloying elements and heat treatment processes which give rise to second phases intermetallic particles (IMPs) also known as intermetallic compounds (IMCs). These second phases play a dominant role in the corrosion susceptibility of aluminum alloys. This review provides a systematic survey of the electrochemical, and galvanic corrosion behavior of IMPs in the context of aluminum alloys. A discussion of the electrochemical/galvanic corrosion behavior of selected/important intermetallic compounds that are commonly found in aluminum alloys such as the Q-phase (Al4Cu2Mg7Si8), π-phase (Al8Mg3FeSi6), θ-phase (Al2Cu), S-phase (Al2CuMg), the β-phase (Mg2Si), β-phase (Al3Mg2), δ (Al3Li), η-phase (MgZn2), and β-phase (Al3Fe) is provided. In addition, the limitations in the electrochemical characterization of intermetallic compounds, the research gap, and prospects are also provided in addition to the phenomenon of galvanic polarity reversal and self-dissolution of IMPs.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are conflicts of interest among the authors.
Figures


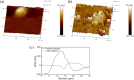

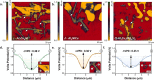
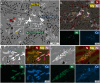

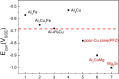











References
-
- Buchheit R. G. A Compilation of Corrosion Potentials Reported for Intermetallic Phases in Aluminum Alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995;142:3994.
-
- Bland L. G. Birbilis N. Scully J. R. Exploring the Effects of Intermetallic Particle Size and Spacing on the Corrosion of Mg–Al Alloys Using Model Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016;163:C895–C906.
-
- Buchheit R. G. et al., Local dissolution phenomena associated with S phase (Al2CuMg) particles in aluminum alloy 2024-T3. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997;144:2621–2628.
-
- Mondolfo L. F., The Aluminum–Magnesium–Zinc, Revere Copper and Brass Inc., Rome, NY, 1967
-
- Birbilis N. Buchheit R. G. Investigation and Discussion of Characteristics for Intermetallic Phases Common to Aluminum Alloys as a Function of Solution pH. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008;155:C117.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

