The role of magnesium in pancreatic beta-cell function and homeostasis
- PMID: 39385789
- PMCID: PMC11463151
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1458700
The role of magnesium in pancreatic beta-cell function and homeostasis
Abstract
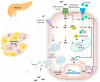
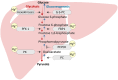
Magnesium plays an essential role in glucose utilization and insulin signaling. Recent advances have revealed a greater prevalence of hypomagnesemia in general, and low intracellular magnesium levels in individuals with diabetes contribute to β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. This article describes the documented effects of magnesium on various aspects of β-cells and glucose homeostasis. Studies have demonstrated that magnesium deficiency is associated with reduced pancreatic β-cell activity and increased insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Additionally, magnesium is involved in many cellular events, including energy homeostasis, protein synthesis, and DNA stability. Furthermore, magnesium is critical for proper glucose utilization and insulin signaling, and magnesium deficiency can lead to the dysregulation of ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels in pancreatic β-cells, impairing insulin secretion. Therefore, maintaining adequate magnesium levels is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing of metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: diabetes; glucose; insulin; magnesium; β-cells.
Copyright © 2024 Akimbekov, Coban, Atfi and Razzaque.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Takaya J, Higashino H, Kobayashi Y. Intracellular magnesium and insulin resistance. Magnes Res. (2004) 17:126–36. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

