Effect of copper on nitrogen uptake, transportation, assimilation processes, and related gene expression in Chinese cabbage [ Brassica campestris L. ssp. Chinensis (L.)] under various nitrate-to-ammonium ratios
- PMID: 39385989
- PMCID: PMC11461266
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1427720
Effect of copper on nitrogen uptake, transportation, assimilation processes, and related gene expression in Chinese cabbage [ Brassica campestris L. ssp. Chinensis (L.)] under various nitrate-to-ammonium ratios
Abstract
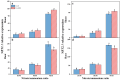
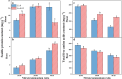
Improving vegetable yield and optimizing its quality through nutrient management have long been central to plant nutrition and horticultural science. Copper (Cu) is recognized as an essential trace element that promotes plant growth and development. However, the mechanisms by which Cu influences nitrogen (N) metabolism remain largely unknown, with limited studies exploring the interaction between Cu and varying nitrate-to-ammonium (nitrate/ammonium) ratios. In this study, Chinese cabbage was exposed to two Cu concentrations (0 and 0.02 mg L-1) in combination with three nitrate/ammonium ratios (10/90, 50/50, and 90/10) under hydroponic conditions. The results showed that Cu application increased plant biomass, nitrate reductase (NR) and glutamine synthetase (GS) enzyme activities, the expression of NR (NIA) and GS2 (Gln2) genes, and N content in both shoots and roots. Additionally, Cu treatment decreased nitrate and free amino acid contents, as well as the expression of nitrate transporters NRT1.1 and NRT2.1 in roots while increasing these four parameters in shoots. Additionally, these effects were significantly modulated by the nitrate/ammonium ratios. In conclusion, Cu may facilitate nitrate transportation, enhance nitrate reduction, promote ammonium assimilation, and influence the transformation of organic N compounds, highlighting its potential role in improving N metabolism in Chinese cabbage.
Keywords: Chinese cabbage; copper; gene expression; nitrate/ammonium ratios; nitrogen metabolism.
Copyright © 2024 Wen, Xu, Tang, Zhong, Chen, Zhu, Zhang, Zhang and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Aghajanzadeh T. A., Prajapati D. H., Burow M. (2020). Copper toxicity affects indolic glucosinolates and gene expression of key enzymes for their biosynthesis in Chinese cabbage. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 66, 1288–1301. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2019.1666208 - DOI
-
- Alhasany A. R., Noaema A. H., Alhmadi H. B. (2019). The role of spraying copper and zinc on the growth and yield of Vicia faba L. Conference Series: Microelectronics Systems Education. 571, 012048. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/571/1/012048 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

