Anti-aging Metabolite-Based Polymeric Microparticles for Intracellular Drug Delivery and Bone Regeneration
- PMID: 39386061
- PMCID: PMC11460827
- DOI: 10.1002/smsc.202400201
Anti-aging Metabolite-Based Polymeric Microparticles for Intracellular Drug Delivery and Bone Regeneration
Abstract
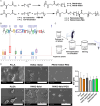
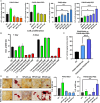
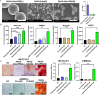
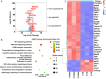
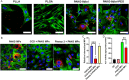
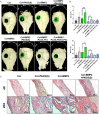
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), a key component of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, has attracted attention for its anti-aging properties. Our recent study indicates that locally delivered cell-permeable AKG significantly promotes osteogenic differentiation and mouse bone regeneration. However, the cytotoxicity and rapid hydrolysis of the metabolite limit its application. In this study, we synthesize novel AKG-based polymeric microparticles (PAKG MPs) for sustained release. In vitro data suggest that the chemical components, hydrophilicity, and size of the MPs can significantly affect their cytotoxicity and pro-osteogenic activity. Excitingly, these biodegradable PAKG MPs are highly phagocytosable for nonphagocytic pre-osteoblasts MC3T3-E1 and primary bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), significantly promoting their osteoblastic differentiation. RNAseq data suggest that PAKG MPs strongly activate Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K-Akt pathways for osteogenic differentiation. Moreover, PAKG enables poly (L-lactic acid) and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) MPs (PLLA & PLGA MPs) for efficient phagocytosis. Our data indicate that PLGA-PAKG MPs-mediated intracellular drug delivery can significantly promote stronger osteoblastic differentiation compared to PLGA MPs-delivered phenamil. Notably, PAKG MPs significantly improve large bone regeneration in a mouse cranial bone defect model. Thus, the novel PAKG-based MPs show great promise to improve osteogenic differentiation, bone regeneration, and enable efficient intracellular drug delivery for broad regenerative medicine.
Keywords: Alpha-ketoglutarate; bone regeneration; intracellular drug delivery; microparticles; osteogenic differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Petite H., Viateau V., Bensaïd W., Meunier A., de Pollak C., Bourguignon M., Oudina K., Sedel L., Guillemin G., Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 959. - PubMed
-
- Ebraheim N. A., Elgafy H., Xu R., J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2001, 9, 210. - PubMed
-
- Martino M. M., Briquez P. S., Maruyama K., Hubbell J. A., Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 94, 41. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
