This is a preprint.
Transcripts with high distal heritability mediate genetic effects on complex metabolic traits
- PMID: 39386475
- PMCID: PMC11463413
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.26.613931
Transcripts with high distal heritability mediate genetic effects on complex metabolic traits
Update in
-
Transcripts with high distal heritability mediate genetic effects on complex metabolic traits.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5507. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61228-9. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40595617 Free PMC article.
Abstract
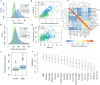
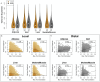
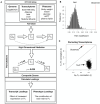
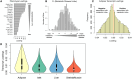
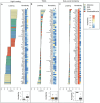
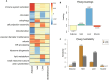
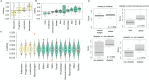
Although many genes are subject to local regulation, recent evidence suggests that complex distal regulation may be more important in mediating phenotypic variability. To assess the role of distal gene regulation in complex traits, we combined multi-tissue transcriptomes with physiological outcomes to model diet-induced obesity and metabolic disease in a population of Diversity Outbred mice. Using a novel high-dimensional mediation analysis, we identified a composite transcriptome signature that summarized genetic effects on gene expression and explained 30% of the variation across all metabolic traits. The signature was heritable, interpretable in biological terms, and predicted obesity status from gene expression in an independently derived mouse cohort and multiple human studies. Transcripts contributing most strongly to this composite mediator frequently had complex, distal regulation distributed throughout the genome. These results suggest that trait-relevant variation in transcription is largely distally regulated, but is nonetheless identifiable, interpretable, and translatable across species.
Figures

References
-
- Maurano M. T., Humbert R., Rynes E., Thurman R. E., Haugen E., Wang H., Reynolds A. P., Sandstrom R., Qu H., Brody J., Shafer A., Neri F., Lee K., Kutyavin T., Stehling-Sun S., Johnson A. K., Canfield T. K., Giste E., Diegel M., Bates D., Hansen R. S., Neph S., Sabo P. J., Heimfeld S., Raubitschek A., Ziegler S., Cotsapas C., Sotoodehnia N., Glass I., Sunyaev S. R., Kaul R., and Stamatoyannopoulos J. A.. Systematic localization of common disease-associated variation in regulatory DNA. Science, 337(6099):1190–1195, Sep 2012. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Farh K. K., Marson A., Zhu J., Kleinewietfeld M., Housley W. J., Beik S., Shoresh N., Whitton H., Ryan R. J., Shishkin A. A., Hatan M., Carrasco-Alfonso M. J., Mayer D., Luckey C. J., Patsopoulos N. A., De Jager P. L., Kuchroo V. K., Epstein C. B., Daly M. J., Hafler D. A., and Bernstein B. E.. Genetic and epigenetic fine mapping of causal autoimmune disease variants. Nature, 518(7539):337–343, Feb 2015. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pennisi E.. The Biology of Genomes. Disease risk links to gene regulation. Science, 332(6033):1031, May 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
