This is a preprint.
Interactions among Merlin, Arkadia, and SKOR2 mediate NF2-associated Schwann cell proliferation in human
- PMID: 39386608
- PMCID: PMC11463491
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.24.614711
Interactions among Merlin, Arkadia, and SKOR2 mediate NF2-associated Schwann cell proliferation in human
Update in
-
Interactions among Merlin, Arkadia, and SKOR2 mediate NF2-associated human Schwann cell proliferation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Apr 5;16(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04281-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40188079 Free PMC article.
Abstract
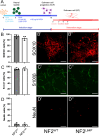
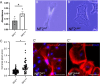
NF2-Related Schwannomatosis (previously referred to as Neurofibromatosis Type 2, or NF2) is a genetic-associated disease resulting from mutations in the gene, NF2. NF2 encodes the merlin protein, which acts as a tumor suppressor. Bilateral vestibular schwannoma (VS) is a hallmark of NF2. Although the exactly molecular mechanism mediating NF2-driven schwannomatosis remain unclear, it is known that defective Merlin protein functionality leads to abnormal cell proliferation. Herein, we utilized a human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-based Schwann cell (SC) model to investigate the role of merlin in human SCs. SCs were derived from hiPSCs carrying a NF2 mutation (c.191 T > C; p. L64P), its isogenic wild-type control cell line, and a NF2 patient-derived hiPSC line. NF2 mutant SCs showed abnormal cellular morphology and proliferation. Proteomic analyses identified novel interaction partners for Merlin - Arkadia and SKOR2. Our results established a new model in which merlin interacts with Arkadia and SKOR2 and this interaction is required for the proper activation of the SMAD-dependent pathway in TGFβ signaling.
Keywords: Arkadia; NF2; NF2-Related Schwannomatosis; SKOR2; Schwann cell; TGFβ; human pluripotent stem cell; merlin; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Brault E G.A., Lamarine M, Callebaut I, Thomas G, Goutebroze L. (2001). Normal membrane localization and actin association of the NF2 tumor suppressor protein are dependent on folding of its N-terminal domain. J Cell Sci 114, 1901–1912. - PubMed
-
- Cho J.H., Oh A.Y., Park S., Kang S.M., Yoon M.H., Woo T.G., Hong S.D., Hwang J., Ha N.C., Lee H.Y., et al. (2018). Loss of NF2 Induces TGFβ Receptor 1-mediated Noncanonical and Oncogenic TGFβ Signaling: Implication of the Therapeutic Effect of TGFβ Receptor 1 Inhibitor on NF2 Syndrome. Mol Cancer Ther 17, 2271–2284. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
