This is a preprint.
miR-21: A therapeutic target for delaying severe liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in high-fat-diet-fed mice
- PMID: 39386656
- PMCID: PMC11463666
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.19.613915
miR-21: A therapeutic target for delaying severe liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in high-fat-diet-fed mice
Abstract
Liver disease, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is a major global health concern, claiming approximately 2 million lives worldwide annually, yet curative treatments remain elusive. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of microRNA-21-5p (miR-21) in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (previously NAFLD), metabolic-associated steatohepatitis (previously NASH), and HCC within the context of a Western high-fat diet, without additional choline (HFD) and offering potential therapeutic insights. We found that reduced miR-21 levels correlated with liver disease progression in WT mice fed on HFD, while miR-21 knockout mice showed exacerbated metabolic dysfunction, including obesity, hepatomegaly, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, steatosis, fibrosis, and HCC. Our study reveals that miR-21 plays a protective role in metabolic syndrome and in the progression of liver disease to cancer. MiR-21 directly targets Transforming growth factor beta-induced (Tgfbi), a gene also known to be significantly upregulated and a potential oncogene in HCC. Further, our study showed that intervention with the administration of a miR-21 mimic in WT livers effectively improves insulin sensitivity, steatosis, fibrosis, Tgfbi expression and tumor burden in HFD conditions. These findings indicate that miR-21 could serve as an effective strategy to delay or prevent liver disease in high-fat-diet environments.
Keywords: MASLD (NAFLD); fibrosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; high-fat diet; liver; miR-21; protective.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Dr. Szabo is a scientific consultant for Durect, Cyta Therapeutics, Pandion, Pfizer, Terra Firma, LabCorp, and Takeda and has stock options in Glympse Bio, Satellite Bio and Ventyx Bio. She received royalties from Springer and UpToDate. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
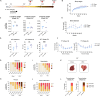



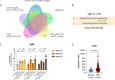

References
-
- Younossi ZM, Wong G, Anstee QM, Henry L. The Global Burden of Liver Disease. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2023. Jul;21(8):1978–91. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023. Jan;73(1):17–48. - PubMed
-
- Rinella ME, Lazarus J V, Ratziu V, Francque SM, Sanyal AJ, Kanwal F, et al. A multi-society Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology. 2023. Jun 24; - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018. Jan;67(1):328–57. - PubMed
-
- Tsochatzis EA. Natural history of NAFLD: knowns and unknowns. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. Mar;19(3):151–2. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
