Novel quinoline-4-carboxamide derivatives potentiates apoptosis by targeting PDK1 to overcome chemo-resistance in colorectal cancer: Theoretical and experimental results
- PMID: 39386832
- PMCID: PMC11462461
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38105
Novel quinoline-4-carboxamide derivatives potentiates apoptosis by targeting PDK1 to overcome chemo-resistance in colorectal cancer: Theoretical and experimental results
Abstract
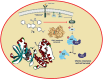
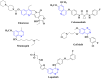
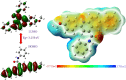
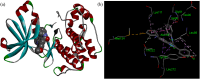
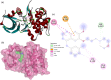
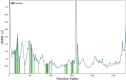
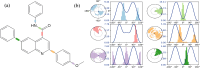
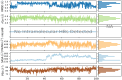
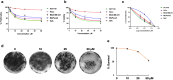
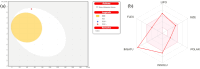
A series of novel N,2-diphenyl-6-(aryl/heteroaryl)quinoline-4-carboxamide derivatives were designed and synthesized using the Suzuki coupling reaction and evaluated them for their anticancer activity. These compounds were screened for anti-colon cancer activity through in-silico studies by molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies. Furthermore, the density functional theory was used to determine the molecule's electrical properties. The molecular electrostatic potential map is used to evaluate the charge distribution on the molecule surface. Unveiling that the compound 7a (binding energy of -10.2 kcal/mol) has good inhibition activity compared to other synthesized compounds (7b-7j) as well as the standard drug Gefitinib. The stability of the compound 7a with the 1OKY protein was confirmed through molecular dynamics simulation studies, indicating potential anti-colon cancer activity against phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1). The in-silico ADMET pharmacokinetic properties indicate adherence to Lipinski's rule of five for favorable safety profiles and the compound falls within the optimal range for physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties, which is comparable to that of the standard medication drug Gefitinib. The synthesized library of compounds was further evaluated for their in-vitro anticancer potency against colon, pancreatic and breast cancer cells. The results demonstrated that the compounds effectively suppressed the proliferative potential of the screened cells in a concentration-dependent manner, as revealed by MTT assay. The anticancer potential of these molecules was further evaluated by acridine orange/PI, and Hoechst/PI which demonstrates the potential of molecules to induce apoptosis in cancer cells. Further investigations and optimization of these derivatives could lead to the development of effective anticancer strategies.
Keywords: ADMET; Chemo-resistance; Colorectal cancer; DFT; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics; PDK1; Quinoline-4-carboxamide derivatives.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Chao A., Thun M.J., Connell C.J., McCullough M.L., Jacobs E.J., Flanders W.D., Rodriguez C., Sinha R., Calle E.E. Meat consumption and risk of colorectal cancer. JAMA. 2005;293:172–182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

