A DNA barcoding framework for taxonomic verification in the Darwin Tree of Life Project
- PMID: 39386966
- PMCID: PMC11462125
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.21143.1
A DNA barcoding framework for taxonomic verification in the Darwin Tree of Life Project
Abstract
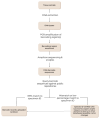
Biodiversity genomics research requires reliable organismal identification, which can be difficult based on morphology alone. DNA-based identification using DNA barcoding can provide confirmation of species identity and resolve taxonomic issues but is rarely used in studies generating reference genomes. Here, we describe the development and implementation of DNA barcoding for the Darwin Tree of Life Project (DToL), which aims to sequence and assemble high quality reference genomes for all eukaryotic species in Britain and Ireland. We present a standardised framework for DNA barcode sequencing and data interpretation that is then adapted for diverse organismal groups. DNA barcoding data from over 12,000 DToL specimens has identified up to 20% of samples requiring additional verification, with 2% of seed plants and 3.5% of animal specimens subsequently having their names changed. We also make recommendations for future developments using new sequencing approaches and streamlined bioinformatic approaches.
Keywords: Britain and Ireland; DNA barcoding; biodiversity; species identification; taxonomy.
Plain language summary
Identifying species based solely on their morphology can be difficult. DNA-based identification using DNA barcoding can aid species identification, but can be challenging to implement in biodiversity projects sampling diverse organismal groups. Here, we describe the development and implementation of DNA barcoding for the Darwin Tree of Life Project (DToL), which aims to sequence and assemble high quality reference genomes for all eukaryotic species in Britain and Ireland. We discuss how a standardised approach has been adapted by each partner to suit different organismal groups, show the efficacy of this approach for confirming species identities and resolving taxonomic issues, and make recommendations for future developments.
Copyright: © 2024 Twyford AD et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Allen DE: The naturalist in Britain: a social history.London: Allen Lane,1976. Reference Source
-
- Cuber P, Chooneea D, Geeves C, et al. : Comparing the accuracy and efficiency of third generation sequencing technologies, Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and Pacific Biosciences, for DNA barcode sequencing applications. Ecol Genet Genom. 2023;28:100181. 10.1016/j.egg.2023.100181 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources