Hemin-induced platelet activation is regulated by the ACKR3 chemokine surface receptor and has implications for passivation of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques
- PMID: 39387619
- PMCID: PMC11653686
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.17294
Hemin-induced platelet activation is regulated by the ACKR3 chemokine surface receptor and has implications for passivation of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques
Abstract
In vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques, intraplaque hemorrhages (IPH) result in hemolysis of red blood cells and release of hemoglobin and free hemin. Hemin activates platelets and leads to thrombosis. Agonism of the inhibitory platelet receptor ACKR3 inhibits hemin-dependent platelet activation and thrombus formation. To characterize the effect of hemin and ACKR3 agonism on isolated human platelets, multi-color flow cytometry and classical experimental setup such as light transmission aggregometry and a flow chamber assay were used. Hemin induces platelet aggregation and ex vivo platelet-dependent thrombus formation on immobilized collagen under a low shear rate of 500 s-1, indicating that free hemin is a strong activator of platelet-dependent thrombosis. Recently, we described that ACKR3 is a prominent inhibitory receptor of platelet activation. Specific ACKR3 agonists but not conventional antiplatelet compounds such as COX-1 inhibitor (indometacin), ADP-receptor blocker (cangrelor), or PAR1 inhibitor (ML161) inhibit both hemin-dependent aggregation and thrombus formation. To further characterize the effect of hemin on platelet subpopulations, we established a multi-color flow cytometry assay. We found that hemin induces procoagulant (CD42bpos/PAC-1neg/AnnexinVpos), aggregatory (CD42bpos/PAC-1pos/AnnexinVneg), and inflammatory (CD42bpos/CXCR4pos/ACKR3pos/AnnexinVpos) platelet subpopulations. Treatment with ACKR3 agonists significantly decreased the formation of procoagulant and ACKR3pos platelets in response to hemin. We conclude that hemin is a strong activator for the formation of procoagulant platelets and thrombus formation which is dependent on the function of ACKR3. Activation of ACKR3 using specific agonists may offer a therapeutic strategy to regulate the vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques in areas of IPH.
Keywords: ACKR3; hemin; intraplaque hemorrhage (IPH); multi‐color flow cytometry; platelets.
© 2024 The Author(s). The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
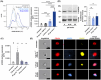
 ), **P < 0.01; ns, not significant. (D) Sample images of dynamic surface expression of CD42b, ACKR3 and CD62P captured by image stream analysis performed with isolated platelets at RT; scale bar = 2 μm; n = 1.
), **P < 0.01; ns, not significant. (D) Sample images of dynamic surface expression of CD42b, ACKR3 and CD62P captured by image stream analysis performed with isolated platelets at RT; scale bar = 2 μm; n = 1.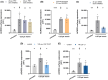
 ), *P < 0.05; ns, not significant. (B) Pre‐incubation with 0.5 μ
), *P < 0.05; ns, not significant. (B) Pre‐incubation with 0.5 μ ), ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant. (C) Pre‐incubation for 15 min with 25 μ
), ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant. (C) Pre‐incubation for 15 min with 25 μ ), *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant. (D) Pre‐incubation for 15 min with 100 μ
), *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant. (D) Pre‐incubation for 15 min with 100 μ ), *P < 0.05. (E) Pre‐incubation for 15 min with 100 μ
), *P < 0.05. (E) Pre‐incubation for 15 min with 100 μ ), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.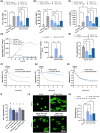
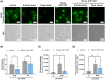

References
-
- Imparato AM, Riles TS & Gorstein F (1979) The carotid bifurcation plaque: pathologic findings associated with cerebral ischemia. Stroke 10, 238–245. - PubMed
-
- Stary HC, Chandler AB, Dinsmore RE, Fuster V, Glagov S, Insull W Jr, Rosenfeld ME, Schwartz CJ, Wagner WD & Wissler RW (1995) A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis. A report from the committee on vascular lesions of the council on arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Circulation 92, 1355–1374. - PubMed
-
- Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340, 115–126. - PubMed
-
- Naghavi M, Libby P, Falk E, Casscells SW, Litovsky S, Rumberger J, Badimon JJ, Stefanadis C, Moreno P, Pasterkamp G et al. (2003) From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: a call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies: part I. Circulation 108, 1664–1672. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

