P2 purinergic receptor expression and function in tumor-related immune cells
- PMID: 39387963
- PMCID: PMC12222599
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-024-10054-7
P2 purinergic receptor expression and function in tumor-related immune cells
Abstract
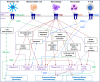
P2 purinergic receptor expression is dysregulated in multiple cancer subtypes and is associated with worse outcomes. Studies identify roles for P2 purinergic receptors in tumor cells that drive disease aggressiveness. There is also sufficient evidence that P2 purinergic receptor expression within the tumor microenvironment (TME) is critical for disease initiation and progression. Immune cells constitute a significant component of the TME and display both tumorigenic and anti-tumorigenic potential. Studies pre-dating the investigation of P2 purinergic receptors in cancer identify P2 receptor expression on multiple immune cells including macrophages, neutrophils, T-cells, and dendritic cells; all of which are implicated in tumor initiation, tumor promotion, or response to treatment. Herein, we discuss P2 purinergic receptor expression and function in tumor-related immune cells. We provide a rationale for further investigations of P2 purinergic receptors within the TME to better define the mechanistic pathways of inflammation-mediate tumorigenesis and explore P2 purinergic receptors as potential targets for novel immunotherapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Immune cells; Macrophages; Neutrophils; P2 purinergic receptor; T-cells; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sarikaya E (2019) Functions of purinergic receptors. In Receptors P1 and P2 as targets for drug therapy in humans, IntechOpen: 2019
-
- da Silva Ferreira NC, Alves LA, Soares-Bezerra RJ (2019) Potential therapeutic applications of P2 receptor antagonists: from bench to clinical trials. Curr Drug Targets 20:919–937 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

