How long do bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses retain their replication capacity on inanimate surfaces? A systematic review examining environmental resilience versus healthcare-associated infection risk by "fomite-borne risk assessment"
- PMID: 39388143
- PMCID: PMC11640306
- DOI: 10.1128/cmr.00186-23
How long do bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses retain their replication capacity on inanimate surfaces? A systematic review examining environmental resilience versus healthcare-associated infection risk by "fomite-borne risk assessment"
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Kramer et al., 'How long do bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses retain their replication capacity on inanimate surfaces? A systematic review examining environmental resilience versus healthcare-associated infection risk by "fomite-borne risk assessment"'.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2025 Sep 11;38(3):e0012925. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00129-25. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40464547 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
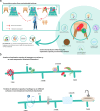
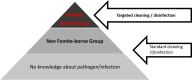
SUMMARYIn healthcare settings, contaminated surfaces play an important role in the transmission of nosocomial pathogens potentially resulting in healthcare-associated infections (HAI). Pathogens can be transmitted directly from frequent hand-touch surfaces close to patients or indirectly by staff and visitors. HAI risk depends on exposure, extent of contamination, infectious dose (ID), virulence, hygiene practices, and patient vulnerability. This review attempts to close a gap in previous reviews on persistence/tenacity by only including articles (n = 171) providing quantitative data on re-cultivable pathogens from fomites for a better translation into clinical settings. We have therefore introduced the new term "replication capacity" (RC). The RC is affected by the degree of contamination, surface material, temperature, relative humidity, protein load, organic soil, UV-light (sunlight) exposure, and pH value. In general, investigations into surface RC are mainly performed in vitro using reference strains with high inocula. In vitro data from studies on 14 Gram-positive, 26 Gram-negative bacteria, 18 fungi, 4 protozoa, and 37 viruses. It should be regarded as a worst-case scenario indicating the upper bounds of risks when using such data for clinical decision-making. Information on RC after surface contamination could be seen as an opportunity to choose the most appropriate infection prevention and control (IPC) strategies. To help with decision-making, pathogens characterized by an increased nosocomial risk for transmission from inanimate surfaces ("fomite-borne") are presented and discussed in this systematic review. Thus, the review offers a theoretical basis to support local risk assessments and IPC recommendations.
Keywords: HAI; bacteria; fomite-borne risk pathogens; fomites; fungi; inanimate surfaces; persistence; protozoa; replication capacity; resilience; tenacity; transmission; viability; viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Carter Y, Barry D. 2011. Tackling C difficile with environmental cleaning. Nurs Times 107:22–25. - PubMed
-
- Cassone M, Zhu Z, Mantey J, Gibson KE, Perri MB, Zervos MJ, Snitkin ES, Foxman B, Mody L. 2020. Interplay between patient colonization and environmental contamination with vancomycin-resistant enterococci and their association with patient health outcomes in postacute care. Open Forum Infect Dis 7:fz519. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofz519 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chmielarczyk A, Higgins PG, Wojkowska-Mach J, Synowiec E, Zander E, Romaniszyn D, Gosiewski T, Seifert H, Heczko P, Bulanda M. 2012. Control of an outbreak of Acinetobacter baumannii infections using vaporized hydrogen peroxide. J Hosp Infect 81:239–245. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2012.05.010 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

