Sitetack: a deep learning model that improves PTM prediction by using known PTMs
- PMID: 39388212
- PMCID: PMC11552626
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae602
Sitetack: a deep learning model that improves PTM prediction by using known PTMs
Abstract
Motivation: Post-translational modifications (PTMs) increase the diversity of the proteome and are vital to organismal life and therapeutic strategies. Deep learning has been used to predict PTM locations. Still, limitations in datasets and their analyses compromise success.
Results: We evaluated the use of known PTM sites in prediction via sequence-based deep learning algorithms. For each PTM, known locations of that PTM were encoded as a separate amino acid before sequences were encoded via word embedding and passed into a convolutional neural network that predicts the probability of that PTM at a given site. Without labeling known PTMs, our models are on par with others. With labeling, however, we improved significantly upon extant models. Moreover, knowing PTM locations can increase the predictability of a different PTM. Our findings highlight the importance of PTMs for the installation of additional PTMs. We anticipate that including known PTM locations will enhance the performance of other proteomic machine learning algorithms.
Availability and implementation: Sitetack is available as a web tool at https://sitetack.net; the source code, representative datasets, instructions for local use, and select models are available at https://github.com/clair-gutierrez/sitetack.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
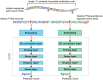
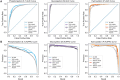
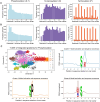
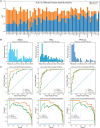
Update of
-
Sitetack: A Deep Learning Model that Improves PTM Prediction by Using Known PTMs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 4:2024.06.03.596298. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.03.596298. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Bioinformatics. 2024 Nov 1;40(11):btae602. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae602. PMID: 38895359 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Sitetack: A Deep Learning Model that Improves PTM Prediction by Using Known PTMs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 4:2024.06.03.596298. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.03.596298. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Bioinformatics. 2024 Nov 1;40(11):btae602. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae602. PMID: 38895359 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
PhosphOrtholog: a web-based tool for cross-species mapping of orthologous protein post-translational modifications.BMC Genomics. 2015 Aug 19;16(1):617. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1820-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26283093 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale comparative assessment of computational predictors for lysine post-translational modification sites.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Nov 27;20(6):2267-2290. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby089. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 30285084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved prediction of post-translational modification crosstalk within proteins using DeepPCT.Bioinformatics. 2024 Nov 28;40(12):btae675. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae675. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 39570595 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications of proteins in cardiovascular diseases examined by proteomic approaches.FEBS J. 2025 Jan;292(1):28-46. doi: 10.1111/febs.17108. Epub 2024 Mar 5. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 38440918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Missense Variant of BMPR1A in Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome: Assessment of Structural and Functional Alternations.Hum Mutat. 2025 Feb 18;2025:7317429. doi: 10.1155/humu/7317429. eCollection 2025. Hum Mutat. 2025. PMID: 40226309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blazev R, , CarlCS, , Ng Y-K. et al. Phosphoproteomics of three exercise modalities identifies canonical signaling and C18ORF25 AS AN AMPK substrate regulating skeletal muscle function. Cell Metab 2022;34:1561–77.e9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

