Sulawesi stream fish communities depend on connectivity and habitat diversity
- PMID: 39388289
- PMCID: PMC11842187
- DOI: 10.1111/jfb.15944
Sulawesi stream fish communities depend on connectivity and habitat diversity
Abstract
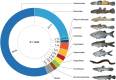
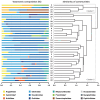
Streams provide an array of habitat niches that may act as environmental filters for fish communities. The tropical island of Sulawesi in Indonesia is located in the Wallacea, a region isolated by marine barriers from the Asian and Australian faunas. Primary freshwater fishes are naturally absent in the Wallacea, including Sulawesi's numerous coastal streams. Diadromous species are in contrast species-rich in the area. The knowledge available on stream fishes in the Wallacea is largely restricted to taxonomic work and studies targeting single species groups, whereas baseline data on fish ecology remain extremely scarce. Such data and a deeper understanding of stream fish ecology are, however, urgently required for purposes such as informed management. We assumed that the stream fish assemblages are dominated by recruitment from the sea and are structured by macro- and microhabitat diversity. To test this hypothesis, we quantified the occurrence of individual fishes by point abundance electrofishing at 33 streams across Sulawesi. The 4632 fishes obtained represent 58 species out of 24 families. The native fishes recorded are mainly amphidromous (34 species), euryhaline (five species), and catadromous (five species). Gobiiformes make up the vast majority of records, dominated by Oxudercidae (22 species) and Eleotridae (five species). Only two of the species recorded are endemic to Sulawesi, including a single species strictly confined to freshwaters. Ten species, making up 6% of the fishes caught, are not native to Sulawesi. The outlying mean index (OMI) and BIOENV analyses suggest that effects on the scale of macro- and microhabitat shape fish assemblage composition, ranging from pH, conductivity, and temperature to current velocity, substrate, canopy cover, and elevation. Habitat niche use of species along the first two OMI axes is complementary and fine-scaled, covering a wide range of the available habitat space. Juvenile and adult conspecifics share similar habitat niches in most of the cases. Niche breadths overlap, but niche specialization is significant in most of the species. Non-native fishes link into the assemblages at the margins of habitat space, with substantial niche overlaps to native species. The present findings show that the native fish communities in coastal streams of Sulawesi are largely composed of species depending on access to the sea, highlighting the importance of connectivity down to the estuaries and sea. The ichthyofauna shows a rich diversity in habitat use, and the availability of alternative habitats along the altitudinal gradient provides plausible filters for species establishment. Non-native fishes are locally abundant, pose substantial potential for changing communities, but are still stocked intentionally. We stress the need for incorporating the need for connectivity and maintained habitat quality into management decisions, and a critical evaluation of stocking activities.
Keywords: community assembly; ecology; freshwater fishes; habitat use; point abundance electrofishing.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Fish Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Fisheries Society of the British Isles.
Figures



References
-
- Arrington, D. A. , Winemiller, K. O. , & Layman, C. A. (2005). Community assembly at the patch scale in a species rich tropical river. Oecologia, 144, 157–167. - PubMed
-
- Askeyev, A. , Askeyev, O. , Yanybaev, N. , Askeyev, I. , Monakhov, S. , Marić, S. , & Hulsman, K. (2017). River fish assemblages along an elevation gradient in the eastern extremity of Europe. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 100, 585–596.
-
- Atminarso, D. , Baumgartner, L. J. , Watts, R. J. , Rourke, M. L. , Bond, J. , & Wibowo, A. (2024). Evidence of fish community fragmentation in a tropical river upstream and downstream of a dam, despite the presence of a fishway. Pacific Conservation Biology, 30(1), 1–11.
-
- Baumgartner, L. J. , & Wibowo, A. (2018). Addressing fish‐passage issues at hydropower and irrigation infrastructure projects in Indonesia. Marine and Freshwater Research, 69(12), 1805–1813.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
