WWC2 modulates GABAA-receptor-mediated synaptic transmission, revealing class-specific mechanisms of synapse regulation by WWC family proteins
- PMID: 39388350
- PMCID: PMC11913214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114841
WWC2 modulates GABAA-receptor-mediated synaptic transmission, revealing class-specific mechanisms of synapse regulation by WWC family proteins
Abstract
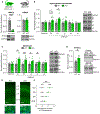
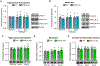
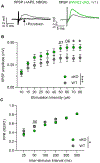
The WW and C2 domain-containing protein (WWC2) is implicated in several neurological disorders. Here, we demonstrate that WWC2 interacts with inhibitory, but not excitatory, postsynaptic scaffolds, consistent with prior proteomic identification of WWC2 as a putative component of the inhibitory postsynaptic density. Using mice lacking WWC2 expression in excitatory forebrain neurons, we show that WWC2 suppresses γ-aminobutyric acid type-A receptor (GABAAR) incorporation into the plasma membrane and regulates HAP1 and GRIP1, which form a complex promoting GABAAR recycling to the membrane. Inhibitory synaptic transmission is increased in CA1 pyramidal cells lacking WWC2. Furthermore, unlike the WWC2 homolog KIBRA (kidney/brain protein; WWC1), a key regulator of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) trafficking at excitatory synapses, the deletion of WWC2 does not affect synaptic AMPAR expression. In contrast, loss of KIBRA does not affect GABAAR membrane expression. These data reveal synapse class-selective functions for WWC proteins as regulators of ionotropic neurotransmitter receptors and provide insight into mechanisms regulating GABAAR membrane expression.
Keywords: AMPA receptor; CP: Neuroscience; GABAA receptor; GRIP1; HAP1; KIBRA; WWC1; WWC2; dendritic arborization; inhibitory synapse; synaptic transmission.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

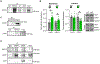

Update of
-
Modulation of GABA A receptor trafficking by WWC2 reveals class-specific mechanisms of synapse regulation by WWC family proteins.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 12:2024.03.11.584487. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.11.584487. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 Oct 22;43(10):114841. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114841. PMID: 38559047 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Vassos E, Bramon E, Picchioni M, Walshe M, Filbey FM, Kravariti E, McDonald C, Murray RM, Collier DA, and Toulopoulou T (2010). Evidence of association of KIBRA genotype with episodic memory in families of psychotic patients and controls. J Psychiatr Res 44, 795–798. 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

