RNA Nanotechnology for Codelivering High-Payload Nucleoside Analogs to Cancer with a Synergetic Effect
- PMID: 39388598
- PMCID: PMC12012820
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00674
RNA Nanotechnology for Codelivering High-Payload Nucleoside Analogs to Cancer with a Synergetic Effect
Abstract
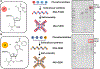
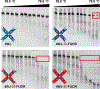
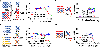
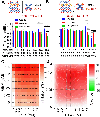
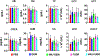
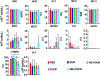
Nucleoside analogs are potent inhibitors for cancer treatment, but the main obstacles to their application in humans are their toxicity, nonspecificity, and lack of targeted delivery tools. Here, we report the use of RNA four-way junctions (4WJs) to deliver two nucleoside analogs, floxuridine (FUDR) and gemcitabine (GEM), with high payloads through routine and simple solid-state RNA synthesis and nanoparticle assembly. The design of RNA nanotechnology for the co-delivery of nucleoside analogs and the chemotherapeutic drug paclitaxel (PTX) resulted in synergistic effects and high efficacy in the treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). The 4WJ-drug complexes were confirmed to have efficient tumor spontaneous targeting and no toxicity because the motility of RNA nanoparticles has been previously shown to enable these RNA-drug complexes to spontaneously accumulate in tumor blood vessels. The negative charge of RNA enables those RNA complexes that are not targeted to tumor vasculature to circulate in the blood and enter the urine through the kidney glomerulus, without accumulating in organs, therefore being nontoxic. Drug incorporation into RNA 4WJ can be precisely controlled with a defined loading amount, location, and ratio. The incorporation of nucleoside analogs into 4WJ only requires one step using nucleoside analogue phosphoramidites during solid-phase RNA synthesis, without the need for additional conjugation and purification processes.
Keywords: RNA nanotechnology; cancer therapy; combinational therapy; drug delivery; floxuridine; gemcitabine; nucleoside analog.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




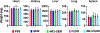
References
-
- Shi J; Kantoff PW; Wooster R; Farokhzad OC Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2017, 17 (1), 20–37. DOI: 10.1038/nrc.2016.108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Torchilin VP Multifunctional, stimuli-sensitive nanoparticulate systems for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2014, 13 (11), 813–827. DOI: 10.1038/nrd4333. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binzel DW; Li X; Burns N; Khan E; Lee W-J; Chen L-C; Ellipilli S; Miles W; Ho YS; Guo P Thermostability, Tunability, and Tenacity of RNA as Rubbery Anionic Polymeric Materials in Nanotechnology and Nanomedicine—Specific Cancer Targeting with Undetectable Toxicity. Chemical Reviews 2021, 121 (13), 7398–7467. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

