BCKDH kinase promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis independent of BCKDHA
- PMID: 39389936
- PMCID: PMC11467410
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-07071-0
BCKDH kinase promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis independent of BCKDHA
Abstract
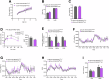
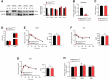
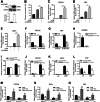
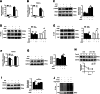
Elevated circulating branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) are tightly linked to an increased risk in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The rate limiting enzyme of BCAA catabolism branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKDH) is phosphorylated at E1α subunit (BCKDHA) by its kinase (BCKDK) and inactivated. Here, the liver-specific BCKDK or BCKDHA knockout mice displayed normal glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. However, knockout of BCKDK in the liver inhibited hepatic glucose production as well as the expression of key gluconeogenic enzymes. No abnormal gluconeogenesis was found in mice lacking hepatic BCKDHA. Consistent with the vivo results, BT2-mediated inhibition or genetic knockdown of BCKDK decreased hepatic glucose production and gluconeogenic gene expressions in primary mouse hepatocytes while BCKDK overexpression exhibited an opposite effect. Whereas, gluconeogenic gene expressions were not altered in BCKDHA-silenced hepatocytes. Mechanistically, BT2 treatment attenuated the interaction of cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) with CREB-binding protein and promoted FOXO1 protein degradation by increasing its ubiquitination. Our findings suggest that BCKDK regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis through CREB and FOXO1 signalings, independent of BCKDHA-mediated BCAA catabolism.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Petersen KF, Price T, Cline GW, Rothman DL, Shulman GI. Contribution of net hepatic glycogenolysis to glucose production during the early postprandial period. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:E186–E191. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82200934/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82170819/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82370798/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 23YF1437600/Shanghai Science and Technology Development Foundation (Shanghai Science and Technology Development Fund)
- 23YF1437600/Shanghai Science and Technology Development Foundation (Shanghai Science and Technology Development Fund)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

