Greylag goose optimization and multilayer perceptron for enhancing lung cancer classification
- PMID: 39390014
- PMCID: PMC11467376
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-72013-x
Greylag goose optimization and multilayer perceptron for enhancing lung cancer classification
Abstract
Lung cancer is an important global health problem, and it is defined by abnormal growth of the cells in the tissues of the lung, mostly leading to significant morbidity and mortality. Its timely identification and correct staging are very important for proper therapy and prognosis. Different computational methods have been used to enhance the precision of lung cancer classification, among which optimization algorithms such as Greylag Goose Optimization (GGO) are employed. These algorithms have the purpose of improving the performance of machine learning models that are presented with a large amount of complex data, selecting the most important features. As per lung cancer classification, data preparation is one of the most important steps, which contains the operations of scaling, normalization, and handling gap factor to ensure reasonable and reliable input data. In this domain, the use of GGO includes refining feature selection, which mainly focuses on enhancing the classification accuracy compared to other binary format optimization algorithms, like bSC, bMVO, bPSO, bWOA, bGWO, and bFOA. The efficiency of the bGGO algorithm in choosing the optimal features for improved classification accuracy is an indicator of the possible application of this method in the field of lung cancer diagnosis. The GGO achieved the highest accuracy with MLP model performance at 98.4%. The feature selection and classification results were assessed using statistical analysis, which utilized the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and ANOVA. The results were also accompanied by a set of graphical illustrations that ensured the adequacy and efficiency of the adopted hybrid method (GGO + MLP).
Keywords: Classification; Feature selection; GGO; Lung cancer; MLP; Optimization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



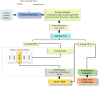

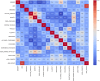


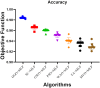

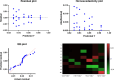





References
-
- Asuntha, A. & Srinivasan, A. Deep learning for lung Cancer detection and classification. Multimed. Tools Appl.79, 7731–7762 (2020).
-
- Chaturvedi, P., Jhamb, A., Vanani, M. & Nemade, V. Prediction and classification of lung cancer using machine learning techniques. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 12059 (IOP Publishing, 2021).
-
- Nanglia, P., Kumar, S., Mahajan, A. N., Singh, P. & Rathee, D. A hybrid algorithm for lung cancer classification using SVM and Neural Networks. ICT Express7(3), 335–341 (2021).
-
- Elshewey, A. M. et al. A Novel WD-SARIMAX model for temperature forecasting using daily Delhi climate dataset. Sustainability15(1), 757 (2022).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

