The mediating effect of circulating inflammatory proteins on the relationship between gut microbiota and FD: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39390038
- PMCID: PMC11466956
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-74717-6
The mediating effect of circulating inflammatory proteins on the relationship between gut microbiota and FD: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
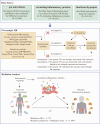
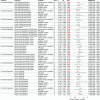
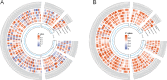
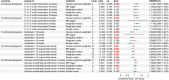
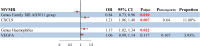
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is known to be influenced by gut microbiota (GM) and circulating inflammatory proteins (CIPs), however, the causal relationship between GM, CIPs and FD haven't been investigated. This study employed two-sample Mendelian Randomization (TSMR) to investigate their associations using data from Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS). In this study, Inverse-variance weighted (IVW) method was employed as the primary analysis, with supplementary approaches including weighted median, weighted mode, simple mode, and MR-Egger. Heterogeneity and pleiotropy were assessed using the Cochrane Q test, MR-Egger intercept test, and MR-PRESSO global test. Totally, 196 GM traits and 91 CIPs were analyzed, and the results uncovered the causal impact of 12 GM taxa and 5 proteins on functional dyspepsia (FD). 9 GM genera were linked to a reduced risk of FD, while 3 GM genera were associated with an increased risk of FD.Additionally, reverse analysis revealed no FD-GM causation. Furthermore, IL-12, IL-10, CXCL10, CXCL9 and VEGFA were significantly correlated with FD, with CXCL9 and VEGFA acting as mediators in the association between GM traits and FD. Taken together, our findings established a link between specific GM and CIPs in the pathogenesis of FD, offering novel insights for its diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: Circulating inflammatory proteins; Functional dyspepsia; Gut microbiota; Mediation analysis; Mendelian randomization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Causal effects between gut microbiota and endometriosis: a two-sample Mendelian randomisation study.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2024 Dec;44(1):2362415. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2024.2362415. Epub 2024 Jun 17. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2024. PMID: 38885114
-
Gut microbiota and intervertebral disc degeneration: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Aug 14;18(1):601. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04081-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37580794 Free PMC article.
-
Causal Effects of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Bidirectional Two Sample Mendelian Randomization Study.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024 Sep 28;19:2153-2167. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S472218. eCollection 2024. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2024. PMID: 39360021 Free PMC article.
-
The gut microbiota and diabetic nephropathy: an observational study review and bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Trials. 2025 Mar 24;26(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13063-025-08755-4. Trials. 2025. PMID: 40122887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the potential causal relationship between gut microbiota and heart failure: A two-sample mendelian randomization study combined with the geo database.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Feb;49(2):102235. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102235. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38040216 Review.
Cited by
-
Mediating role of circulating inflammatory proteins in the effect of immune cells on esophageal cancer risk: A Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e40374. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040374. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39496002 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Inflammatory Proteins Mediate the Causal Effect of Gut Microbiota on Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Bayesian and Mediated Mendelian Randomization.FASEB Bioadv. 2025 Jul 10;7(7):e70039. doi: 10.1096/fba.2025-00114. eCollection 2025 Jul. FASEB Bioadv. 2025. PMID: 40654330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oshima, T. Functional dyspepsia: current understanding and future perspective. Digestion105(1), 26–33 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Romano, C. et al. Functional dyspepsia: an Enigma in a conundrum. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr.63(6), 579–584 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Zhang, J. et al. Insights and future prospects of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of functional dyspepsia. Phytomedicine. 127, 155481 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Sayuk, G. S. et al. Functional dyspepsia: diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Drugs80(13), 1319–1336 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82274630/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- GZY-KJS-2020-077/the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- y2018rc05/the Peak Academic Talents in Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- QN202308/Youth Talent Project of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicinegrant number
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
- BK20240741/Natural Science Youth Foundation of Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

