Transplacental SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF8 binds to complement C1q to trigger fetal inflammation
- PMID: 39390219
- PMCID: PMC11574245
- DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00260-9
Transplacental SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF8 binds to complement C1q to trigger fetal inflammation
Abstract
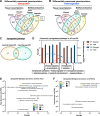
Prenatal SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with higher rates of pregnancy and birth complications, despite that vertical transmission rates are thought to be low. Here, multi-omics analyses of human placental tissues, cord tissues/plasma, and amniotic fluid from 23 COVID-19 mother-infant pairs revealed robust inflammatory responses in both maternal and fetal compartments. Pronounced expression of complement proteins (C1q, C3, C3b, C4, C5) and inflammatory cytokines (TNF, IL-1α, and IL-17A/E) was detected in the fetal compartment of COVID-19-affected pregnancies. While ~26% of fetal tissues were positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA, more than 60% of fetal tissues contained SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 proteins, suggesting transplacental transfer of this viral accessory protein. ORF8-positive fetal compartments exhibited increased inflammation and complement activation compared to ORF8-negative COVID-19 pregnancies. In human placental trophoblasts in vitro, exogenous ORF8 exposure resulted in complement activation and inflammatory responses. Co-immunoprecipitation analysis demonstrated that ORF8 binds to C1q specifically by interacting with a 15-peptide region on ORF8 (C37-A51) and the globular domain of C1q subunit A. In conclusion, an ORF8-C1q-dependent complement activation pathway was identified in COVID-19-affected pregnancies, likely contributing to fetal inflammation independently of fetal virus exposure.
Keywords: Classical Complement Activation; Fetal Inflammation; Pregnancy; SARS-CoV-2; Transplacental ORF8.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures















References
-
- Amari Chinchilla K, Vijayan M, Taveras Garcia B, Jim B (2020) Complement-mediated disorders in pregnancy. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 27:155–164 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00DE028573/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDR)
- R01 AI116585/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI140705,R01AI140718,R01AI116585,AI140718,AI172252/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- AI129534,AI298847,AI140718,AI172252,AI140718,AI172252/HHS | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 AI140718/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE033391/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- RES515531/Clinical and Translational Science Center, Weill Cornell Medicine (CTSC)
- R21 AI129534/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI140705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DE028573/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DE033391/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDR)
- S10 OD023436/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI172252/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004528/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

