RNA-Seq analysis for breast cancer detection: a study on paired tissue samples using hybrid optimization and deep learning techniques
- PMID: 39390265
- PMCID: PMC11467072
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-05968-z
RNA-Seq analysis for breast cancer detection: a study on paired tissue samples using hybrid optimization and deep learning techniques
Abstract
Problem: Breast cancer is a leading global health issue, contributing to high mortality rates among women. The challenge of early detection is exacerbated by the high dimensionality and complexity of gene expression data, which complicates the classification process.
Aim: This study aims to develop an advanced deep learning model that can accurately detect breast cancer using RNA-Seq gene expression data, while effectively addressing the challenges posed by the data's high dimensionality and complexity.
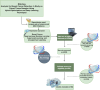
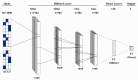
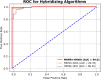
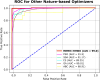
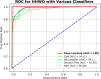
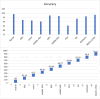
Methods: We introduce a novel hybrid gene selection approach that combines the Harris Hawk Optimization (HHO) and Whale Optimization (WO) algorithms with deep learning to improve feature selection and classification accuracy. The model's performance was compared to five conventional optimization algorithms integrated with deep learning: Genetic Algorithm (GA), Artificial Bee Colony (ABC), Cuckoo Search (CS), and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). RNA-Seq data was collected from 66 paired samples of normal and cancerous tissues from breast cancer patients at the Jawaharlal Nehru Cancer Hospital & Research Centre, Bhopal, India. Sequencing was performed by Biokart Genomics Lab, Bengaluru, India.
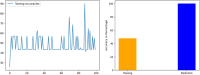
Results: The proposed model achieved a mean classification accuracy of 99.0%, consistently outperforming the GA, ABC, CS, and PSO methods. The dataset comprised 55 female breast cancer patients, including both early and advanced stages, along with age-matched healthy controls.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrate that the hybrid gene selection approach using HHO and WO, combined with deep learning, is a powerful and accurate tool for breast cancer detection. This approach shows promise for early detection and could facilitate personalized treatment strategies, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Deep learning; Harris Hawk algorithm; Whale optimization algorithm.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author confirms that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Novel Breast Cancer Diagnosis Scheme With Intelligent Feature and Parameter Selections.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022 Feb;214:106432. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106432. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022. PMID: 34844767
-
A bio-inspired convolution neural network architecture for automatic breast cancer detection and classification using RNA-Seq gene expression data.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 5;13(1):14644. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41731-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37670037 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid GAN-based deep learning framework for thermogram-based breast cancer detection.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 4;15(1):19665. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04676-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40467954 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid machine learning feature selection model-HMLFSM to enhance gene classification applied to multiple colon cancers dataset.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 2;18(11):e0286791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286791. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37917732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning approaches for breast cancer detection in histopathology images: A review.Cancer Biomark. 2024;40(1):1-25. doi: 10.3233/CBM-230251. Cancer Biomark. 2024. PMID: 38517775 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Feature Selection in Breast Cancer Gene Expression Data Using KAO and AOA with SVM Classification.J Med Syst. 2025 Mar 26;49(1):40. doi: 10.1007/s10916-025-02171-6. J Med Syst. 2025. PMID: 40140121
-
Variation in bulk RNA-seq and estimated cell type proportion using deconvolution when comparing pancreatic cancer samples within the same individual.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 6:2025.05.05.25326976. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.05.25326976. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40385431 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Advanced machine learning framework for enhancing breast cancer diagnostics through transcriptomic profiling.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 17;16(1):334. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02111-3. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40095253 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming Cancer Classification: The Role of Advanced Gene Selection.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Nov 22;14(23):2632. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232632. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682540 Free PMC article.
-
Improving stroke risk prediction by integrating XGBoost, optimized principal component analysis, and explainable artificial intelligence.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025 Feb 7;25(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12911-025-02894-z. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025. PMID: 39920691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdollahzadeh B et al (2024) Puma optimizer (PO): a novel metaheuristic optimization algorithm and its application in machine learning. Cluster Comput 27(4):5235–5283. 10.1007/s10586-023-04221-5
-
- Agrawal P, Abutarboush HF, Ganesh T, Mohamed AW (2021) Metaheuristic algorithms on feature selection: a survey of one decade of research (2009–2019). IEEE Access 9:26766–26791. 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3056407
-
- Alabool HM, Alarabiat D, Abualigah L, Heidari AA (2021) Harris hawks optimization: a comprehensive review of recent variants and applications. Neural Comput Appl 33(15):8939–8980. 10.1007/s00521-021-05720-5
-
- Algamal ZY, Lee MH (2015) Regularized logistic regression with adjusted adaptive elastic net for gene selection in high dimensional cancer classification. Comput Biol Med 67:136–145. 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.10.008 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

