AIMP2 accumulation in brain leads to cognitive deficits and blood secretion in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39390613
- PMCID: PMC11465931
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05666-x
AIMP2 accumulation in brain leads to cognitive deficits and blood secretion in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Propagation of neuronal α-synuclein aggregate pathology to the cortex and hippocampus correlates with cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease (PD) dementia and dementia with Lewy body disease. Previously, we showed accumulation of the parkin substrate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase interacting multifunctional protein-2 (AIMP2) in the temporal lobe of postmortem brains of patients with advanced PD. However, the potential pathological role of AIMP2 accumulation in the cognitive dysfunction of patients with PD remains unknown.
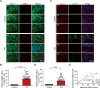
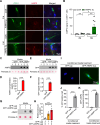
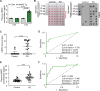
Methods: We performed immunofluorescence imaging to examine cellular distribution and accumulation of AIMP2 in brains of conditional AIMP2 transgenic mice and postmortem PD patients. The pathological role of AIMP2 was investigated in the AIMP2 transgenic mice by assessing Nissl-stained neuron counting in the hippocampal area and Barnes maze to determine cognitive functions. Potential secretion and cellular uptake of AIMP2 was monitored by dot blot analysis and immunofluorescence. The utility of AIMP2 as a new PD biomarker was evaluated by dot blot and ELISA measurement of plasma AIMP2 collected from PD patients and healthy control followed by ROC curve analysis.
Results: We demonstrated that AIMP2 is toxic to the dentate gyrus neurons of the hippocampus and that conditional AIMP2 transgenic mice develop progressive cognitive impairment. Moreover, we found that neuronal AIMP2 expression levels correlated with the brain endothelial expression of AIMP2 in both AIMP2 transgenic mice and in the postmortem brains of patients with PD. AIMP2, when accumulated, was released from the neuronal cell line SH-SY5Y cells. Secreted AIMP2 was taken up by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Consistent with the fact that AIMP2 can be released into the extracellular space, we showed that AIMP2 transgenic mice have higher levels of plasma AIMP2. Finally, ELISA-based assessment of AIMP2 in plasma samples from patients with PD and controls, and subsequent ROC curve analysis proved that high plasma AIMP2 expression could serve as a reliable molecular biomarker for PD diagnosis.
Conclusions: The pathological role in the hippocampus and the cell-to-cell transmissibility of AIMP2 provide new therapeutic avenues for PD treatment, and plasma AIMP2 combined with α-synuclein may improve the accuracy of PD diagnosis in the early stages.
Keywords: AIMP2; Blood biomarker; Conditional transgenic mice; Diagnosis; Intercellular protein transmission; Lewy body dementia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.H., and Y.L. are inventors of the patent related to this work (South Korea domestic patent no. 10-2252879, “Method for diagnosing Parkinson’s disease using AIMP2 in blood plasma, composition therefor and kit containing the same”). The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

