Causal effect of thyroid cancer on secondary primary malignancies: findings from the UK Biobank and FinnGen cohorts
- PMID: 39391305
- PMCID: PMC11464368
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1434737
Causal effect of thyroid cancer on secondary primary malignancies: findings from the UK Biobank and FinnGen cohorts
Abstract
Background: Existing epidemiological data indicated a correlation between thyroid cancer (THCA) and the risk of secondary primary malignancies (SPMs). However, the correlation does not always imply causality.
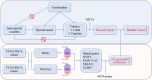
Methods: The Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses were performed to investigate the causal relationships between THCA and SPMs based on international multicenter data. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) were calculated. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) was used to explore potential mechanisms shared by THCA and bladder cancer (BLCA).
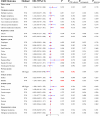
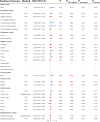
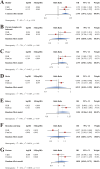
Results: Summary datasets of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) on 30 types of cancers were obtained from the United Kingdom Biobank (UKB) and FinnGen database. Meta-analysis of the UKB and FinnGen results revealed that THCA was significantly positively correlated with BLCA (OR = 1.140; 95% CI, 1.072-1.212; P < 0.001). Four genes, including WNT3, FAM171A2, MLLT11, and ULBP1, were identified as key genes shared by both TCHA and BLCA. Correlation analysis indicated that THCA may increase the risk of secondary BLCA through augmentation of N2 neutrophil infiltration.
Conclusions: This study showed that THCA was causally related to BLCA. It is recommended to conduct more rigorous screenings for BLCA during the follow-up of THCA patients.
Keywords: GWAS; Mendelian randomization; SNP; bladder cancer; thyroid cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Rixiati, Jia, Xu, Yin, Huang, Dai and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Giovanella L, Garo ML, Campenni A, Petranovic Ovcaricek P, Gorges R. Thyroid hormone withdrawal versus recombinant human TSH as preparation for I-131 therapy in patients with metastatic thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:2510. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092510 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

