Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of Dendrobium chrysotoxum and D. thyrsiflorum reveal the biosynthetic pathway from gigantol to erianin
- PMID: 39391777
- PMCID: PMC11464314
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1436560
Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of Dendrobium chrysotoxum and D. thyrsiflorum reveal the biosynthetic pathway from gigantol to erianin
Abstract
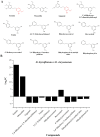
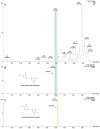
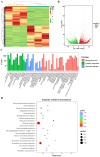
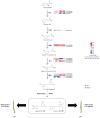
Erianin is one of the most representative bibenzyls with significant inhibitory activity against a wide range of tumor cells. However, the low erianin level in natural materials has severely inhibited its further development in health care. Our aim was to uncover the erianin biosynthetic pathway to lay the foundation for promoting its production. Firstly, we screened and obtained two Dendrobium species (Dendrobium thyrsiflorum stems with lower erianin content and D. chrysotoxum stems with higher erianin content), belonging to the same Dendrobium section (Chrysotoxae). A systematic analysis of bibenzyl structure and content in two stems revealed that gigantol might be an erianin biosynthetic intermediate, which was verified by introducing deuterium-labeled gigantol. Chemical structure analyses indicated that gigantol was modified by two kinds of enzymes (hydroxylases and O-methyltransferases), leading to erianin synthesis. Up-regulated hydroxylases and O-methyltransferases (OMTs) were screened out and were performed by molecular docking simulation experiments. We propose a rational biosynthetic pathway from gigantol to erianin, as well as relevant enzymes involved in the process. Our findings should significantly contribute to comprehensive resolution of the erianin biosynthetic pathway, promote its large-scale industrial production as well as contribute to biosynthesis studies of other bibenzyls.
Keywords: biosynthetic pathway; dendrobium; erainin; metabolomics; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2024 Xie, Chen, Cheng, Zhang, Ma, Zhang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- An T. N. M., Cuong N. V., Quang N. M., Thanh T. V., Alam M. J. C. (2020). Green synthesis using PEG-400 catalyst, antimicrobial activities, cytotoxicity and in silico molecular docking of new carbazole based on α-aminophosphonate. Chemistryselect 5, 6339–6349. doi: 10.1002/slct.202000855 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

