Atractylodes Lancea and Its Constituent, Atractylodin, Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via AMPK Activation
- PMID: 39391981
- PMCID: PMC11535289
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.083
Atractylodes Lancea and Its Constituent, Atractylodin, Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via AMPK Activation
Abstract
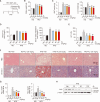
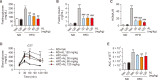
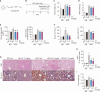
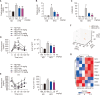
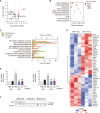
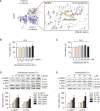
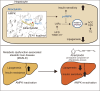
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), which encompasses a spectrum of conditions ranging from simple steatosis to hepatocellular carcinoma, is a growing global health concern associated with insulin resistance. Since there are limited treatment options for MASLD, this study investigated the therapeutic potential of Atractylodes lancea, a traditional herbal remedy for digestive disorders in East Asia, and its principal component, atractylodin, in treating MASLD. Following 8 weeks of high-fat diet (HFD) feeding, mice received oral doses of 30, 60, or 120 mg/kg of Atractylodes lancea. In HFD-fed mice, Atractylodes lancea treatment reduced the body weight; serum triglyceride, total cholesterol, and alanine aminotransferase levels; and hepatic lipid content. Furthermore, Atractylodes lancea significantly ameliorated fasting serum glucose, fasting serum insulin, and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance levels in response to HFD. Additionally, a glucose tolerance test demonstrated improved glucose homeostasis. Treatment with 5 or 10 mg/kg atractylodin also resulted in anti-obesity, anti-steatosis, and glucose-lowering effects. Atractylodin treatment resulted in the downregulation of key lipogenic genes (Srebf1, Fasn, Scd2, and Dgat2) and the upregulation of genes regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α. Notably, the molecular docking model suggested a robust binding affinity between atractylodin and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Atractylodin activated AMPK, which contributed to SREBP1c regulation. In conclusion, our results revealed that Atractylodes lancea and atractylodin activated the AMPK signaling pathway, leading to improvements in HFD-induced obesity, fatty liver, and glucose intolerance. This study suggests that the phytochemical, atractylodin, can be a treatment option for MASLD.
Keywords:
AMP-activated protein kinase;
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong M. J., Gaunt P., Aithal G. P., Barton D., Hull D., Parker R., Hazlehurst J. M., Guo K. LEAN trial team, author; Abouda, G., Aldersley, M. A., Stocken, D., Gough, S. C., Tomlinson, J. W., Brown, R. M., Hubscher, S. G., Newsome, P. N., author Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. 2016;387:679–690. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

