Innovative sample preparation using alcohol dehydration and high refractive index medium enables acquisition of two-channel super-resolution 3D STED image of an entire oocyte
- PMID: 39392013
- PMCID: PMC11733846
- DOI: 10.1111/jmi.13363
Innovative sample preparation using alcohol dehydration and high refractive index medium enables acquisition of two-channel super-resolution 3D STED image of an entire oocyte
Abstract
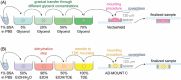
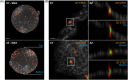
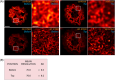
Super-resolution (SR) microscopy is a cutting-edge method that can provide detailed structural information with high resolution. However, the thickness of the specimen has been a major limitation for SR methods, and large biological structures have posed a challenge. To overcome this, the key step is to optimise sample preparation to ensure optical homogeneity and clarity, which can enhance the capabilities of SR methods for the acquisition of thicker structures. Oocytes are the largest cells in the mammalian body and are crucial objects in reproductive biology. They are especially useful for studying membrane proteins. However, oocytes are extremely fragile and sensitive to mechanical manipulation and osmotic shocks, making sample preparation a critical and challenging step. We present an innovative, simple and sensitive approach to oocyte sample preparation for 3D STED acquisition. This involves alcohol dehydration and mounting into a high refractive index medium. This extended preparation procedure allowed us to successfully obtain a unique two-channel 3D STED SR image of an entire mouse oocyte. By optimising sample preparation, it is possible to overcome current limitations of SR methods and obtain high-resolution images of large biological structures, such as oocytes, in order to study fundamental biological processes. Lay Abstract: Super-resolution (SR) microscopy is a cutting-edge tool that allows scientists to view incredibly fine details in biological samples. However, it struggles with larger, thicker specimens, as they need to be optically clear and uniform for the best imaging results. In this study, we refined the sample preparation process to make it more suitable for SR microscopy. Our method includes carefully dehydrating biological samples with alcohol and then transferring them into a mounting medium that enhances optical clarity. This improved protocol enables high-resolution imaging of thick biological structures, which was previously challenging. By optimizing this preparation method, we hope to expand the use of SR microscopy for studying large biological samples, helping scientists better understand complex biological structures.
Keywords: 3D STED; alcohol dehydration; high refractive index medium; large biological objects; oocyte; sample preparation; super‐resolution.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Microscopy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Royal Microscopical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hell, S. W. , & Wichmann, J. (1994). Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: Stimulated‐emission‐depletion fluorescence microscopy. Optics Letters, 19(11), 780–782. - PubMed
-
- Klar, T. A. , Engel, E. , & Hell, S. W. (2001). Breaking Abbe's diffraction resolution limit in fluorescence microscopy with stimulated emission depletion beams of various shapes. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 64(6 Pt 2), 066613. - PubMed
-
- Hell, S. W. (2009). Microscopy and its focal switch. Nature Methods, 6(1), 24–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

