Fully Automated Artificial Intelligence Solution for Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Immunohistochemistry Scoring in Breast Cancer: A Multireader Study
- PMID: 39393036
- PMCID: PMC11485213
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.24.00353
Fully Automated Artificial Intelligence Solution for Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Immunohistochemistry Scoring in Breast Cancer: A Multireader Study
Abstract
Purpose: The proven efficacy of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) antibody-drug conjugate therapy for treating HER2-low breast cancers necessitates more accurate and reproducible HER2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) scoring. We aimed to validate performance and utility of a fully automated artificial intelligence (AI) solution for interpreting HER2 IHC in breast carcinoma.
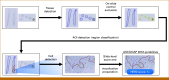
Materials and methods: A two-arm multireader study of 120 HER2 IHC whole-slide images from four sites assessed HER2 scoring by four surgical pathologists without and with the aid of an AI HER2 solution. Both arms were compared with high-confidence ground truth (GT) established by agreement of at least four of five breast pathology subspecialists according to ASCO/College of American Pathologists (CAP) 2018/2023 guidelines.
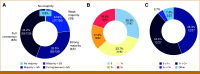
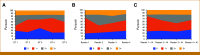
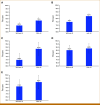
Results: The mean interobserver agreement among GT pathologists across all HER2 scores was 72.4% (N = 120). The AI solution demonstrated high accuracy for HER2 scoring, with 92.1% agreement on slides with high confidence GT (n = 92). The use of the AI tool led to improved performance by readers, interobserver agreement increased from 75.0% for digital manual read to 83.7% for AI-assisted review, and scoring accuracy improved from 85.3% to 88.0%. For the distinction of HER2 0 from 1+ cases (n = 58), pathologists supported by AI showed significantly higher interobserver agreement (69.8% without AI v 87.4% with AI) and accuracy (81.9% without AI v 88.8% with AI).
Conclusion: This study demonstrated utility of a fully automated AI solution to aid in scoring HER2 IHC accurately according to ASCO/CAP 2018/2023 guidelines. Pathologists supported by AI showed improvements in HER2 IHC scoring consistency and accuracy, especially for distinguishing HER2 0 from 1+ cases. This AI solution could be used by pathologists as a decision support tool for enhancing reproducibility and consistency of HER2 scoring and particularly for identifying HER2-low breast cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
References
-
- Wolff AC, Somerfield MR, Dowsett M, et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: ASCO-College of American Pathologists guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:3867–3872. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpma/pma.cfm?id5p990... US Food and Drug Medical Device Database of premarket approvals.
-
- Pantanowitz L, Quiroga-Garza GM, Bien L, et al. An artificial intelligence algorithm for prostate cancer diagnosis in whole slide images of core needle biopsies: A blinded clinical validation and deployment study. Lancet Digit Health. 2020;2:e407–e416. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

