Structure function analysis of ADP-dependent cyanobacterial phosphofructokinase reveals new phylogenetic grouping in the PFK-A family
- PMID: 39393572
- PMCID: PMC11609450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107868
Structure function analysis of ADP-dependent cyanobacterial phosphofructokinase reveals new phylogenetic grouping in the PFK-A family
Abstract
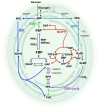
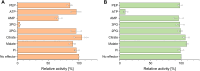
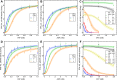
Depending on the light conditions, photosynthetic organisms switch between carbohydrate synthesis or breakdown, for which the reversibility of carbohydrate metabolism, including glycolysis, is essential. Kinetic regulation of phosphofructokinase (PFK), a key-control point in glycolysis, was studied in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. The two PFK iso-enzymes (PFK- A1, PFK-A2), were found to use ADP instead of ATP, and have similar kinetic characteristics, but differ in their allosteric regulation. PFK-A1 is inhibited by 3-phosphoglycerate, a product of the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle, while PFK-A2 is inhibited by ATP, which is provided by photosynthesis. This regulation enables cyanobacteria to switch PFK off in light, and on in darkness. ADP dependence has not been reported before for the PFK-A enzyme family and was thought to be restricted to the PFK-B ribokinase superfamily. Phosphate donor specificity within the PFK-A family could be related to specific binding motifs in ATP-, ADP-, and PPi-dependent PFK-As. Phylogenetic analysis revealed a distribution of ADP-PFK-As in cyanobacteria and in a few alphaproteobacteria, which was confirmed in enzymatic studies.
Keywords: ADP; ADP-dependent PFK-A; ATP; PFK-A superfamily; PPi signature binding motifs; allosteric regulation; cyanobacteria.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
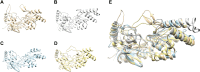

References
-
- Schulze D., Kohlstedt M., Becker J., Cahoreau E., Peyriga L., Makowka A., et al. GC/MS-based 13C metabolic flux analysis resolves the parallel and cyclic photomixotrophic metabolism of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 Selected Deletion Mutants Including Entner-doudoroff Phosphoketolase Pathways. Microb. Cell Fact. 2022;21:69. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Makowka A., Nichelmann L., Schulze D., Spengler K., Wittmann C., Forchhammer K., et al. Glycolytic shunts replenish the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle as anaplerotic reactions in cyanobacteria. Mol. Plant. 2020;13:471–482. - PubMed
-
- Yang C., Hua Q., Shimizu K. Integration of the information from gene expression and metabolic fluxes for the analysis of the regulatory mechanisms in Synechocystis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002;58:813–822. - PubMed
-
- Knowles V.L., Plaxton W.C. From genome to enzyme: analysis of key glycolytic and oxidative pentose-phosphate pathway enzymes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003;44:758–763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

