The outcome of advanced and recurrent cervical cancer patients treated with first-line platinum and paclitaxel with or without indication for immune checkpoint inhibitors: the comparative study
- PMID: 39394089
- PMCID: PMC11468096
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12989-x
The outcome of advanced and recurrent cervical cancer patients treated with first-line platinum and paclitaxel with or without indication for immune checkpoint inhibitors: the comparative study
Abstract
Objective: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy activates the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells that have escaped surveillance. This study aimed to compare the treatment outcome of advanced and recurrent cervical cancer patients treated with first-line platinum and paclitaxel with or without ICI.
Methods: Data from 69 advanced and recurrent cervical cancer patients treated with first-line ICI plus platinum and paclitaxel (N = 33) or first-line platinum and paclitaxel (N = 36) were reviewed between March 2020 and January 2023 in this retrospective study. Patients chose treatment based on the actual disease condition, patient willingness, and medical advice. Additionally, objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were calculated, and adverse events were gained.
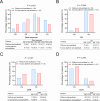
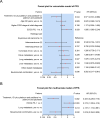
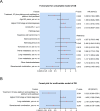
Results: There was no difference in baseline data between patients receiving the two different treatments (all P > 0.05). Complete response rate (18.2% vs. 8.3%; P = 0.294), ORR (48.5% vs. 30.6%; P = 0.127), and DCR (81.8% vs. 72.2%; P = 0.345) tended to ascend in patients treated with ICI plus platinum and paclitaxel compared to those treated with platinum and paclitaxel, although there was no statistical significance. In patients treated with ICI plus platinum and paclitaxel, the median PFS was 10.3 months and the median OS was not reached. Meanwhile, the median PFS and OS were 7.7 and 16.9 months in patients treated with platinum and paclitaxel. PFS (P = 0.036) and OS (P = 0.033) were increased in patients treated with ICI plus platinum and paclitaxel versus those treated with platinum and paclitaxel, which was verified by multivariate Cox regression analyses (both P < 0.05). No difference was observed in the occurrence of adverse events between patients receiving the two different treatments (all P > 0.05).
Conclusion: First-line ICI plus platinum and paclitaxel yields better treatment responses, longer survival, and non-differential adverse events versus first-line platinum and paclitaxel in advanced and recurrent cervical cancer patients.
Keywords: Advanced and recurrent cervical cancer; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Safety; Survival; Treatment response.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures