Histone lysine methylation modifiers controlled by protein stability
- PMID: 39394462
- PMCID: PMC11541785
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01329-5
Histone lysine methylation modifiers controlled by protein stability
Abstract
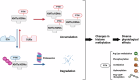
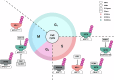
Histone lysine methylation is pivotal in shaping the epigenetic landscape and is linked to cell physiology. Coordination of the activities of multiple histone lysine methylation modifiers, namely, methyltransferases and demethylases, modulates chromatin structure and dynamically alters the epigenetic landscape, orchestrating almost all DNA-templated processes, such as transcription, DNA replication, and DNA repair. The stability of modifier proteins, which is regulated by protein degradation, is crucial for their activity. Here, we review the current knowledge of modifier-protein degradation via specific pathways and its subsequent impact on cell physiology through epigenetic changes. By summarizing the functional links between the aberrant stability of modifier proteins and human diseases and highlighting efforts to target protein stability for therapeutic purposes, we aim to promote interest in defining novel pathways that regulate the degradation of modifiers and ultimately increase the potential for the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Biggar, K. K. & Li, S. S. C. Non-histone protein methylation as a regulator of cellular signalling and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.16, 5–17 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

