Associations between plasma markers and symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with breast cancer
- PMID: 39394561
- PMCID: PMC11468209
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-024-06143-x
Associations between plasma markers and symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with breast cancer
Abstract
Background and purpose: Among patients with solid tumors, those with breast cancer (BC) experience the most severe psychological issues, exhibiting a high global prevalence of depression that negatively impacts prognosis. Depression can be easily missed, and clinical markers for its diagnosis are lacking. Therefore, this study in order to investigate the diagnostic markers for BC patients with depression and anxiety and explore the specific changes of metabolism.
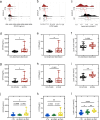
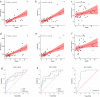
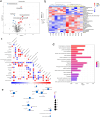
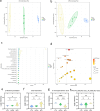
Method and results: Thirty-eight BC patients and thirty-six matched healthy controls were included in the study. The anxiety and depression symptoms of the participants were evaluated by the 17-item Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD-17) and Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA). Plasma levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and lipocalin-2 (LCN2) were evaluated using enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, and plasma lactate levels and metabolic characteristics were analyzed.
Conclusion: This study revealed that GFAP and LCN2 may be good diagnostic markers for anxiety or depression in patients with BC and that plasma lactate levels are also a good diagnostic marker for anxiety. In addition, specific changes in metabolism in patients with BC were preliminarily explored.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Diagnosis; Metabolism; Mood; Patients.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ding X, Wu M, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Han Y, Wang G, Xiao G, Teng F, Wang J, Chen J, et al. The prevalence of depression and suicidal ideation among cancer patients in mainland China and its provinces, 1994–2021: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 201 cross-sectional studies. J Affect Disord. 2023;323:482–9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

