Genetic architectures of the human hippocampus and those involved in neuropsychiatric traits
- PMID: 39394562
- PMCID: PMC11470718
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03682-8
Genetic architectures of the human hippocampus and those involved in neuropsychiatric traits
Abstract
Background: The hippocampus, with its complex subfields, is linked to numerous neuropsychiatric traits. While most research has focused on its global structure or a few specific subfields, a comprehensive analysis of hippocampal substructures and their genetic correlations across a wide range of neuropsychiatric traits remains underexplored. Given the hippocampus's high heritability, considering hippocampal and subfield volumes (HASV) as endophenotypes for neuropsychiatric conditions is essential.
Methods: We analyzed MRI-derived volumetric data of hippocampal and subfield structures from 41,525 UK Biobank participants. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) on 24 HASV traits were conducted, followed by genetic correlation, overlap, and Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses with 10 common neuropsychiatric traits. Polygenic risk scores (PRS) based on HASV traits were also evaluated for predicting these traits.
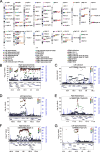
Results: Our analysis identified 352 independent genetic variants surpassing a significance threshold of 2.1 × 10-9 within the 24 HASV traits, located across 93 chromosomal regions. Notably, the regions 12q14.3, 17q21.31, 12q24.22, 6q21, 9q33.1, 6q25.1, and 2q24.2 were found to influence multiple HASVs. Gene set analysis revealed enrichment of neural differentiation and signaling pathways, as well as protein binding and degradation. Of 240 HASV-neuropsychiatric trait pairs, 75 demonstrated significant genetic correlations (P < 0.05/240), revealing 433 pleiotropic loci. Particularly, genes like ACBD4, ARHGAP27, KANSL1, MAPT, ARL17A, and ARL17B were involved in over 50 HASV-neuropsychiatric pairs. Leveraging Mendelian randomization analysis, we further confirmed that atrophy in the left hippocampus, right hippocampus, right hippocampal body, and right CA1-3 region were associated with an increased risk of developing Parkinson's disease (PD). Furthermore, PRS for all four HASVs were significantly linked to a higher risk of Parkinson's disease (PD), with the highest hazard ratio (HR) of 1.30 (95% CI 1.18-1.43, P = 6.15 × 10⁻⁸) for right hippocampal volume.
Conclusions: These findings highlight the extensive distribution of pleiotropic genetic determinants between HASVs and neuropsychiatric traits. Moreover, they suggest a significant potential for effectively managing and intervening in these diseases during their early stages.
Keywords: Hippocampus; Neuropsychiatric; Parkinson’s disease; Pleiotropic.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Burgess N, Maguire EA, O’Keefe J. The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron. 2002;35:625–41. - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Jiménez EP, Flor-García M, Terreros-Roncal J, Rábano A, Cafini F, Pallas-Bazarra N, et al. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med. 2019;25:554–60. - PubMed
-
- Calabresi P, Castrioto A, Di Filippo M, Picconi B. New experimental and clinical links between the hippocampus and the dopaminergic system in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:811–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- NSFC-82003547, NSFC-82373663/Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- NSFC-82103929, NSFC-82273713/Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- WJ2023M045/rogram of Health Commission of Hubei Province
- 2023020201020244/Knowledge Innovation Program of Wuhan
- 2023020201010060/Knowledge Innovation Program of Wuhan
- whkxjsj011, 2023020201010073/Knowledge Innovation Program of Wuhan
- 2022YFA0806601/National Key R&D Program of China
- NSFC-81925032/National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China
- NSFC-82130098/Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- EWT2173/the Leading Talent Program of the Health Commission of Hubei Province
- 2042022rc0026, 2042023kf1005/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 2042024kf1012/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 2022QNRC001/Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST
- 2023AFA046/National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Hubei Province of China
- NSFC-82322058/National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

