Diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate ameliorates salt tolerance associated with ion transport, osmotic adjustment, and metabolite reprograming in white clover
- PMID: 39394568
- PMCID: PMC11470666
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-024-05657-6
Diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate ameliorates salt tolerance associated with ion transport, osmotic adjustment, and metabolite reprograming in white clover
Abstract
Background: Soil salinization is a serious environmental hazard, limiting plant growth and production in different agro-ecological zones worldwide. Diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate (DA-6) as an essential plant growth regulator (PGR) exhibits a beneficial role in improving crop growth and stress tolerance. However, the DA-6-regulated effect and mechanism of salt tolerance in plants are still not fully understood. The objective of current study was to disclose salt tolerance induced by DA-6 in relation to changes in water and redox balance, photosynthetic function, ionic homeostasis, and organic metabolites reprogramming in white clover (Trifolium repens).
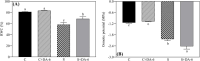
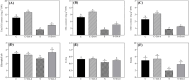
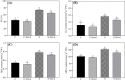
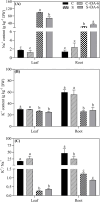
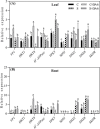
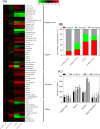
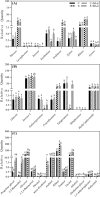
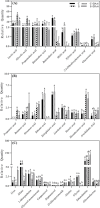
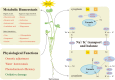
Results: A prolonged duration of salt stress caused water loss, impaired photosynthetic function, and oxidative injury to plants. However, foliar application of DA-6 significantly improved osmotic adjustment (OA), photochemical efficiency, and cell membrane stability under salt stress. In addition, high salinity induced massive accumulation of sodium (Na), but decreased accumulation of potassium (K) in leaves and roots of all plants. DA-6-treated plants demonstrated significantly higher transcript levels of genes involved in uptake and transport of Na and K such as VP1, HKT8, SOS1, NHX2, NHX6, and SKOR in leaves as well as VP1, HKT1, HKT8, H+-ATPase, TPK5, SOS1, NHX2, and SKOR in roots. Metabolomics analysis further illustrated that DA-6 primarily induced the accumulation of glucuronic acid, hexanoic acid, linolenic acid, arachidonic acid, inosose, erythrulose, galactopyranose, talopyranose, urea, 1-monopalmitin, glycerol monostearate, campesterol, stigmasterol, and alanine.
Conclusions: The DA-6 significantly up-regulated transcript levels of multiple genes associated with increased Na+ compartmentalization in vacuoles and Na+ sequestration in roots to reduce Na+ transport to photosynthetic organs, thereby maintaining Na+ homeostasis under salt stress. The accumulation of many organic metabolites induced by the DA-6 could be attributed to enhanced cell wall and membrane structural stability and functionality, OA, antioxidant defense, and downstream signal transduction in leaves under salt stress. The present study provides a deep insight about the synergistic role of DA-6 in salt tolerance of white clover.
Keywords: Gene expression; Ionic homeostasis; Metabolomics; Organic acids; SOS pathway; Sugars.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bouaziz M, Hihi S, Chtourou MY, Osunmadewa B. Soil salinity detection in semi-arid region using spectral unmixing, remote sensing and ground truth measurements. J Geographic Inform Syst. 2020;12(4):372–86. - DOI
-
- FAO. The state of the world’s land and water resources for food and agriculture—systems at breaking point. Rome: 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

