Faster and Safer "In situ" Synthesis of Germanane and Silicane
- PMID: 39394817
- PMCID: PMC11926497
- DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202400964
Faster and Safer "In situ" Synthesis of Germanane and Silicane
Abstract
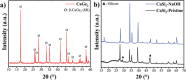
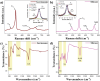
Germanane (GeH) and silicane (SiH), members of the Xanes family, have garnered significant attention as 2D materials due to their diverse properties, which hold promise for applications in electronics, optoelectronics, energy storage, and sensing. Typically, highly concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl) or hydrofluoric acid (HF) is employed in the synthesis of these Xanes, but both routes are problematic due to slow kinetics and safety concerns, respectively. Here for the first time, a faster and safer method is demonstrated for Xanes synthesis that harnesses the generation of HF "in situ" using a solution of HCl and lithium fluoride (LiF) salt, overcoming the key challenges of the conventional methods. A variety of characterization techniques to establish a baseline is utilized for both Xanes and to provide a holistic knowledge regarding this method, the possible consequences of this approach, and the possibility of applying it to other layered Zintl phases. The novel synthesis protocol results in high-quality GeH and SiH with bandgaps (Eg) of 1.75 and 2.47 eV respectively, highlighting their potential suitability for integration into semiconductor applications.
Keywords: 2D materials; Xanes; germanane; silicane; synthesis; “in situ” HF.
© 2024 The Author(s). Small Methods published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- a) Zhang W.‐B., Song Z.‐B., Dou L.‐M., J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 3087;
- b) Madhushankar B. N., Kaverzin A., Giousis T., Potsi G., Gournis D., Rudolf P., Blake G. R., van der Wal C. H., van Wees B. J., 2D Mater. 2017, 4, 021009.
-
- a) Ko S. B., Sun Y., Park G., Choi H. J., Kim J. G., Kim J. B., Jung H. J., Lee G. S., Hong S., Padmajan Sasikala S., Kim S. O., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 32707; - PubMed
- b) Stavrou M., Papadakis I., Stathis A., Kloberg M. J., Mock J., Kratky T., Gunther S., Rieger B., Becherer M., Lyuleeva‐Husemann A., Couris S., J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 815. - PubMed
-
- a) Krishnamoorthy K., Pazhamalai P., Kim S.‐J., Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1595;
- b) Loaiza L. C., Monconduit L., Seznec V., J. Power Sources 2019, 417, 99;
- c) Pazhamalai P., Krishnamoorthy K., Sahoo S., Mariappan V. K., Kim S. J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 624; - PubMed
- d) Gao R., Tang J., Yu X., Lin S., Zhang K., Qin L. C., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002200.
-
- a) Zhao F., Feng Y., Wang Y., Zhang X., Liang X., Li Z., Zhang F., Wang T., Gong J., Feng W., Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1443; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Liu Z., Lou Z., Li Z., Wang G., Wang Z., Liu Y., Huang B., Xia S., Qin X., Zhang X., Dai Y., Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11046; - PubMed
- c) Jia C., Zhang F., She L., Li Q., He X., Sun J., Lei Z., Liu Z. H., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 11257; - PubMed
- d) Giousis T., Fang S., Miola M., Li S., Lazanas A., Prodromidis M., Tekelenburg E. K., Moschovas D., Loi M. A., Rudolf P., Gournis D., Pescarmona P. P., J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109784.
-
- Vogt P., De Padova P., Quaresima C., Avila J., Frantzeskakis E., Asensio M. C., Resta A., Ealet B., Le Lay G., Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 155501. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- EP/L01548X/1/Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council
- EP/S021531/1/Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council
- Henry Royce Institute and the National Graphene Institute
- EP/R00661X/1/Henry Royce Institute for Advanced Materials
- EP/S019367/1/Henry Royce Institute for Advanced Materials
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

