Nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery in the vascular system: focus on endothelium
- PMID: 39396002
- PMCID: PMC11470712
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-024-02892-9
Nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery in the vascular system: focus on endothelium
Abstract
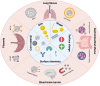
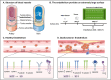
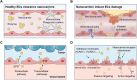
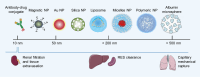
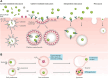
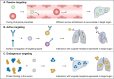
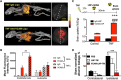
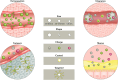
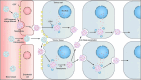
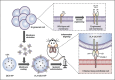
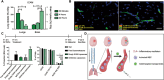
Endothelial cells (ECs) are pivotal in maintaining vascular health, regulating hemodynamics, and modulating inflammatory responses. Nanocarriers hold transformative potential for precise drug delivery within the vascular system, particularly targeting ECs for therapeutic purposes. However, the complex interactions between vascular ECs and nanocarriers present significant challenges for the development and clinical translation of nanotherapeutics. This review assesses recent advancements and key strategies in employing nanocarriers for drug delivery to vascular ECs. It suggested that through precise physicochemical design and surface modifications, nanocarriers can enhance targeting specificity and improve drug internalization efficiency in ECs. Additionally, we elaborated on the applications of nanocarriers specifically designed for targeting ECs in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, cancer metastasis, and inflammatory disorders. Despite these advancements, safety concerns, the complexity of in vivo processes, and the challenge of achieving subcellular drug delivery remain significant obstacles to the effective targeting of ECs with nanocarriers. A comprehensive understanding of endothelial cell biology and its interaction with nanocarriers is crucial for realizing the full potential of targeted drug delivery systems.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Drug targeting; Nanocarriers; Nanomedicine; Vascular endothelial cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JJKH20231222KJ/Science and Technology Research Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province
- 2021YFA1100700/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2022DJ02/Department of Human Resource and Social Security of Jilin Province
- 2022JBGS01/Bethune Medical Department of Jilin University
- JLSWSRCZX2023-81/Medical and Health Talent Special Project of Jilin Province
- 2022YYGFZJC006/Jilin University First Hospital and Academician Chen Xuesi's Team Joint Laboratory Interdisciplinary Project
- 2024B03/Bethune Plan Project of Jilin University
- 82325029/National Outstanding Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- U22A20156/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

