Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac stromal cells up-regulate cardiomyocyte protective responses to hypoxia
- PMID: 39396003
- PMCID: PMC11470622
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-024-03983-y
Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac stromal cells up-regulate cardiomyocyte protective responses to hypoxia
Abstract
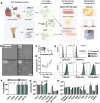
Background: Cell therapy can protect cardiomyocytes from hypoxia, primarily via paracrine secretions, including extracellular vesicles (EVs). Since EVs fulfil specific biological functions based on their cellular origin, we hypothesised that EVs from human cardiac stromal cells (CMSCLCs) obtained from coronary artery bypass surgery may have cardioprotective properties.
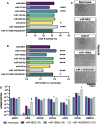
Objectives: This study characterises CMSCLC EVs (C_EVs), miRNA cargo, cardioprotective efficacy and transcriptomic modulation of hypoxic human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs). C_EVs are compared to bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell EVs (B_EVs) which are a known therapeutic EV type.
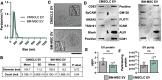
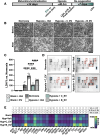
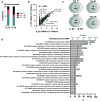
Methods: Cells were characterised for surface markers, gene expression and differentiation potential. EVs were compared for yield, phenotype, and ability to protect hiPSC-CMs from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. EV dose was normalised by both protein concentration and particle count, allowing direct comparison. C_EV and B_EV miRNA cargo was profiled and RNA-seq was performed on EV-treated hypoxic hiPSC-CMs, then data were integrated by multi-omics. Confirmatory experiments were carried out using miRNA mimics.
Results: At the same dose, C_EVs were more effective than B_EVs at protecting CM integrity, reducing apoptotic markers, and cell death during hypoxia. While C_EVs and B_EVs shared 70-77% similarity in miRNA content, C_EVs contained unique miRNAs, including miR-202-5p, miR-451a and miR-142-3p. Delivering miRNA mimics confirmed that miR-1260a and miR-202/451a/142 were cardioprotective, and the latter upregulated protective pathways similar to whole C_EVs.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the potential of cardiac tissues, routinely discarded following surgery, as a valuable source of EVs for myocardial infarction therapy. We also identify miR-1260a as protective of CM hypoxia.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Exosome; Mesenchymal stromal cell; Multi-omics; RNA-sequencing; miRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barile L, Moccetti T, Marbán E, Vassalli G. Roles of exosomes in cardioprotection. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:1372–9. - PubMed
-
- Tariq U, Gupta M, Pathak S, Patil R, Dohare A, Misra SK. Role of Biomaterials in Cardiac Repair and Regeneration: therapeutic intervention for myocardial infarction. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022;8:3271–98. - PubMed
-
- Han MA, Jeon JH, Shin JY, Kim HJ, Lee JS, Seo CW, et al. Intramyocardial delivery of human cardiac stem cell spheroids with enhanced cell engraftment ability and cardiomyogenic potential for myocardial infarct repair. J Controlled Release. 2021;336:499–509. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

