Time delayed fractional diabetes mellitus model and consistent numerical algorithm
- PMID: 39396062
- PMCID: PMC11470918
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-74767-w
Time delayed fractional diabetes mellitus model and consistent numerical algorithm
Abstract
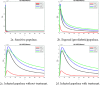
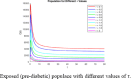
The diabetes mellitus model (DMM) is explored in this study. Many health issues are caused by this disease. For this reason, the integer order DMM is converted into the time delayed fractional order model by fitting the fractional order Caputo differential operator and delay factor in the model. It is proved that the generalized model has the advantage of a unique solution for every time t. Moreover, every solution of the system is positive and bounded. Two equilibrium states of the fractional model are worked out i.e. disease free equilibrium state and the endemic equilibrium state. The risk factor indicator, R0 is computed for the system. The stability analysis is carried out for the underlying system at both the equilibrium states. The key role of R0 is investigated for the disease dynamics and stability of the system. The hybridized finite difference numerical method is formulated for obtaining the numerical solutions of the delayed fractional DMM. The physical features of the numerical method are examined. Simulated graphs are presented to assess the biological behavior of the numerical method. Lastly, the outcomes of the study are furnished in the conclusion section.
Keywords: Fractional time delayed differential equation; GL non-standard finite difference schemes; Global stability.; LaSalle principal; Volterra type Lyapunov function.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Awad, S. F., Critchley, J. A. & Abu-Raddad, L. J. Epidemiological impact of targeted interventions for people with diabetes mellitus on Tuberculosis transmission in India: Modelling-based predictions. Epidemics. 30, 100381. 10.1016/j.epidem.2019.100381 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Al-Hussein, A. B. A., Rahma, F. & Jafari, S. Hopf bifurcation and chaos in a time-delay model of the glucose-insulin regulatory system. Chaos Solit Fract. 137, 109845. 10.1016/j.chaos (2020). 2020.109845. - DOI
-
- Abidemi, A., Owolabi, K. M. & Pindza, E. Modelling the transmission dynamics of Lassa fever with nonlinear incidence rate and vertical transmission. Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 597, 127259. 10.1016/j.physa.2022.127259 (2022). - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical