Using widely targeted metabolomics profiling to explore differences in constituents of three Bletilla species
- PMID: 39396087
- PMCID: PMC11470930
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-74204-y
Using widely targeted metabolomics profiling to explore differences in constituents of three Bletilla species
Abstract
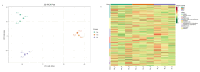
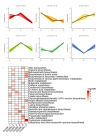
Bletilla striata has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for thousands of years to treat a variety of health diseases. Currently, metabolic causes of differences in medicinal values are unknown, due to the lack of a large-scale and comprehensive investigation of metabolites in Bletilla species. In order to gain a better understanding of the major chemical constituents responsible for the medicinal value, this study aimed to explore the metabolomic differences among three Bletilla species (Bletilla striata: Bs, Bletilla ochracea: Bo and Bletilla formosana: Bf). There were 258 different metabolites between 'Bo' and 'Bf', the contents of 109 metabolites had higher abundance, while 149 metabolites showed less accumulation. There were 165 different metabolites between the 'Bs' and 'Bf', content of 72 metabolites was increased and content of 93 metabolites was decreased. There were 239 different metabolites between the 'Bs' and 'Bo', content of 145 metabolites was increased and content of 94 metabolites was decreased. In the Bo_vs_Bf, Bs_vs_Bf and Bs_vs_Bo groups, the major differential categories were flavonoids, phenolic acids, organic acids and alkaloids. Moreover, the differential metabolites were clustered into clear and distinct profiles via K-means analysis. In addition, the major differential categories were flavonoids, phenolic acids, organic acids and alkaloids. The 'Flavonoid biosynthesis' (ko00941) and 'Phenylalanine metabolism' (ko00360) pathways were significantly enriched in Bo_vs_Bf, Bs_vs_Bf and Bs_vs_Bo comparisons. These results clarify the metabolomics in different Bletilla species, as well as providing basis for the phamaceutical value of novel species of Bletilla.
Keywords: Bletilla formosana; Bletilla ochracea; Bletilla striata; Chinese traditional medicine; Metabolites.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The medicinal uses of the genus Bletilla in traditional Chinese medicine: A phytochemical and pharmacological review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;280:114263. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114263. Epub 2021 Jun 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34144194
-
Screening of Bletilla striata, Bletilla ochracea and Oreorchis foliosa differential metabolites based on metabolomics.Biomed Chromatogr. 2022 Jul;36(7):e5376. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5376. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Biomed Chromatogr. 2022. PMID: 35338508
-
Ultrasound-assisted metabolite detection in different extraction processes of Bletilla striata and bitter metabolite detection.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Mar;114:107266. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107266. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 39952165 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Metabolite Profile Changes in Semen Ziziphi Spinosae During Ripening.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2025 Apr 15;39(11):e10024. doi: 10.1002/rcm.10024. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2025. PMID: 40105258
-
Bletilla striata: Medicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 4;195:20-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.11.026. Epub 2016 Nov 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27865796 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative metabolome and transcriptome analysis of foxtail millet cultivars with high and low grain quality.Food Chem (Oxf). 2025 May 2;10:100259. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2025.100259. eCollection 2025 Jun. Food Chem (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 40475248 Free PMC article.
-
GC-MS based nutritional and aroma profiling of date palm seeds collected from different Egyptian cultivars for valorization purposes.Sci Rep. 2025 May 13;15(1):16531. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00171-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40360602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hossain, M. M. Therapeutic orchids: traditional uses and recent advances—An overview. Fitoterapia82(2), 102–140 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Yang, L. et al. A new macrolide and six cycloartane triterpenoids from the tubers of Bletilla striata. Biochem. Syst. Ecol.57, 238–241 (2014).
-
- Hew, C. S. & Yong, J. The physiology of tropical orchids in relation to the industry: The physiology of tropical orchids in relation to the industry (2004).
-
- Jiang, S., Wang, M., Jiang, L., Xie, Q. & Wang, W. The medicinal uses of the genus Bletilla in traditional Chinese medicine: A phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 114263. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

