Targeting Hypoxia and Autophagy Inhibition via Delivering Sonodynamic Nanoparticles With HIF-2α Inhibitor for Enhancing Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 39396375
- PMCID: PMC11670269
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202402973
Targeting Hypoxia and Autophagy Inhibition via Delivering Sonodynamic Nanoparticles With HIF-2α Inhibitor for Enhancing Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
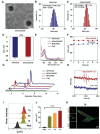
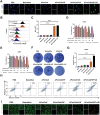
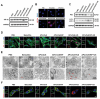
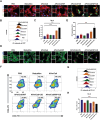
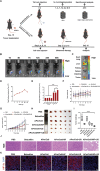
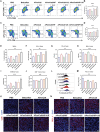
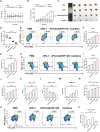
Immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs) therapy stands as the first-line treatment option for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, its effectiveness is hindered by the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME). Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) generates tumor cell fragments that can prime the host's antitumor immunity. Nevertheless, the hypoxic microenvironment and upregulated autophagy following SDT often lead to cancer cell resistance. In response to these challenges, a hypoxia-responsive polymer (Poly(4,4'-azobisbenzenemethanol-PMDA)-mPEG5k, P-APm) encapsulating both a HIF-2α inhibitor (belzutifan) and the ultrasonic sensitize (Chlorin e6, Ce6) is designed, to create the nanoparticle APm/Ce6/HIF. APm/Ce6/HIF combined with ultrasound (US) significantly suppresses tumor growth and activates antitumor immunity in vivo. Moreover, this treatment effectively transforms the immunosuppressive microenvironment from "immune-cold" to "immune-hot", thereby enhancing the response to ICBs therapy. The findings indicate that APm/Ce6/HIF offers a synergistic approach combining targeted therapy with immunotherapy, providing new possibilities for treating RCC.
Keywords: HIF‐2α; immunotherapy; renal cell carcinoma; sonodynamic therapy.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., Wagle N. S., Jemal A., CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17. - PubMed
-
- Bukavina L., Bensalah K., Bray F., Carlo M., Challacombe B., Karam J A., Kassouf W., Mitchell T., Montironi R., O'Brien T., Panebianco V., Scelo G., Shuch B., van Poppel H., Blosser C D., Psutka S P., Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 529. - PubMed
-
- a) Yan X. Q., Ye M. J., Zou Q., Chen P., He Z. S., Wu B., He D. L., He C. H., Xue X. Y., Ji Z. G., Chen H., Zhang S., Liu Y. P., Zhang X. D., Fu C., Xu D. F., Qiu M. X., Lv J. J., Huang J., Ren X. B., Cheng Y., Qin W. J., Zhang X., Zhou F. J., Ma L. L., Guo J. M., Ding D. G., Wei S. Z., He Y., Guo H. Q., et al., Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 190; - PubMed
- b) Peng Y. L., Xiong L. B., Zhou Z. H., Ning K., Li Z., Wu Z. S., Deng M. H., Wei W. S., Wang N., Zou X. P., He Z. S., Huang J. W., Luo J. H., Liu J. Y., Jia N., Cao Y., Han H., Guo S. J., Dong P., Yu C. P., Zhou F. J., Zhang Z. L., J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004206. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Atkins M. B., Jegede O. A., Haas N. B., McDermott D. F., Bilen M. A., Stein M., Sosman J. A., Alter R., Plimack E. R., Ornstein M., Hurwitz M., Peace D. J., Signoretti S., Denize T., Cimadamore A., Wu C. J., Braun D., Einstein D., Catalano P. J., Hammers H., J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2913; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Pal S. K., McGregor B., Suárez C., Tsao C. K., Kelly W., Vaishampayan U., Pagliaro L., Maughan B. L., Loriot Y., Castellano D., Srinivas S., McKay R. R., Dreicer R., Hutson T., Dubey S., Werneke S., Panneerselvam A., Curran D., Scheffold C., Choueiri T. K., Agarwal N., J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3725; - PMC - PubMed
- c) McDermott D. F., Lee J. L., Bjarnason G. A., Larkin J. M. G., Gafanov R. A., Kochenderfer M. D., Jensen N. V., Donskov F., Malik J., Poprach A., Tykodi S. S., Alonso‐Gordoa T., Cho D. C., Geertsen P. F., Climent Duran M. A., DiSimone C., Silverman R. K., Perini R. F., Schloss C., Atkins M B., J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1020. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

